A strategic guide for procurement managers, operations directors, and sustainability officers in the hospitality & foodservice industries.
The restaurant industry is at a pivotal moment, with sustainability evolving from a niche concern to a core operational imperative. As procurement managers, operations directors, sustainability officers, and supply chain executives, you are tasked with meeting heightened consumer demand for eco-conscious practices while navigating complex regulations and supply chain realities. The shift away from single-use plastics, particularly straws, is no longer optional—it’s a strategic necessity that impacts market positioning, compliance, and ultimately, profitability.
Ignoring this trend carries significant operational and commercial risks, from hefty regulatory fines to a tarnished brand image among an increasingly discerning customer base. This guide provides a strategic framework for sourcing eco-friendly straws in bulk, ensuring compliance, enhancing your brand, and contributing meaningfully to a greener future.
I. The Urgent Need for Eco-Friendly Straws: Market & Regulatory Pressure
The momentum for eco-friendly straws is undeniable, propelled by powerful market dynamics and an evolving regulatory landscape. Businesses that fail to adapt risk falling behind, losing market share, and facing legal repercussions.
A. Market Growth & Consumer Demand Driving Eco-Friendly Straws Adoption
The global foodservice industry is undergoing a profound transformation, with sustainable practices at its core. The global sustainable foodservice packaging market was estimated atUSD 62.89 billion in 2024, with projections indicating a substantial rise toUSD 105.54 billion by 2033, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.92% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is directly influenced by the burgeoning eco-friendly straw market itself, which is projected to reach25.1 مليار دولار أمريكي بحلول عام 2035(CAGR of 7.3%), fueled by rising demand for sustainable products.
This robust market expansion is underpinned by a critical shift in consumer behavior. A striking80% of consumers now prefer eco-friendly products, a preference that directly influences their dining choices and restaurant loyalty. The expansion of quick-service restaurants (QSRs) and the sustained growth of online food delivery platforms further intensify the demand for sustainable disposable solutions, making the transition to eco-friendly straws not just a choice, but a competitive imperative.
B. Regulatory Landscape & Plastic Straw Bans Shaping Procurement
Regulatory bodies globally are taking decisive action against single-use plastics, fundamentally reshaping procurement strategies for the foodservice industry. TheEuropean Union banned single-use plastic straws effective July 3, 2021, a landmark directive specifically targeting items that constitute 70% of marine litter. This aggressive stance by a major economic bloc serves as a precedent for global policy.
Similar legislative actions are accelerating across the United States. Several U.S. states, including California, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Washington, have implemented statewide plastic straw bans or “upon request” policies. Cities like San Francisco have gone even further, requiringBiodegradable Products Institute (BPI) or TÜV AUSTRIA certified compostablefoodware, and explicitly prohibiting littered “compostable plastics” that can act like conventional plastic, underscoring the need for certified, truly degradable alternatives. In Asia, Taiwan aims toeliminate all single-use plastic straws by 2025, a policy with significant implications for its bustling bubble tea industry and other sectors. These regulations are not merely suggestions; they are mandates that directly impact a restaurant’s operational legality and market access.
C. Environmental Imperative: The Cost of Inaction on Plastic Waste
Beyond market demand and regulatory pressure, the environmental toll of traditional plastic straws presents a compelling argument for immediate action. An estimated8.3 billion plastic straws have polluted beaches since 2019, with a staggering8 million tons of plastic entering oceans annually. This unchecked pollution has severe ecological consequences: over1.1 million marine mammals are reportedly killed each year by plastic debris, highlighting the devastating impact on biodiversity.
Traditional plastic straws, made from non-renewable fossil resources, takeup to 200 years to decompose, fragmenting into persistent microplastics that infiltrate ecosystems and the food chain. Their production also contributes to toxic combustion byproducts when incinerated. Switching to eco-friendly alternatives dramatically reduces reliance on finite resources, mitigates toxic emissions, and directly combats the pervasive issue of plastic pollution, contributing to a healthier planet and a more resilient future for the industry.
Embracing eco-friendly straws is crucial for restaurants to meet consumer demand and comply with evolving global regulations.
II. Decoding Eco-Friendly Straw Materials: Performance & Compliance
Navigating the array of eco-friendly straw materials requires a deep understanding of their performance characteristics, environmental benefits, and compliance nuances. Decision-makers must select options that align with operational needs, customer expectations, and regulatory requirements.
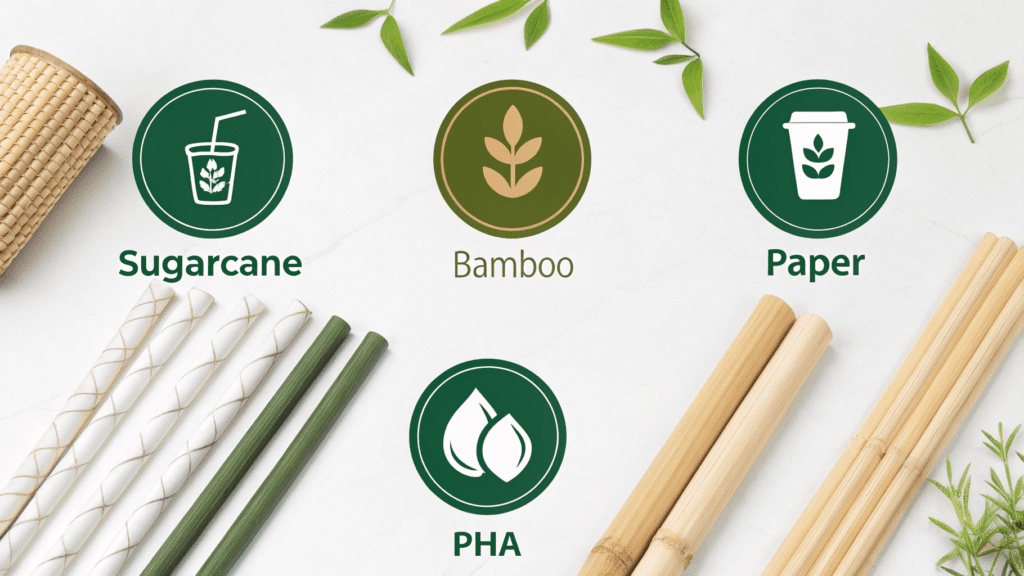

A. Paper Straws: A Common Transition with Evolving Performance
Paper straws represent one of the most common initial transitions for businesses moving away from plastic. They are widely available, typically100% biodegradable, and compostable, often made from Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)-certified paper, signaling responsible sourcing. In industrial composting environments, they biodegrade naturally in45-90 days, a significant improvement over plastic.
Early versions of paper straws were widely criticized forsogginessand premature disintegration, negatively impacting the customer experience. However, modern designs have addressed these concerns with enhanced durability and moisture resistance, often through innovative coatings. A critical concern remains the potential presence ofPFAS “forever chemicals”in some paper straws, used for water resistance, which has prompted FDA phase-out discussions and demands for stringent supplier scrutiny to ensure genuinely safe and eco-friendly products.
B. Plant-Based Bioplastics: PLA, PHA, Sugarcane, Agave
The evolution of bioplastics offers advanced solutions that often mimic the feel and performance of traditional plastic while being environmentally responsible.
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) Straws: Derived from renewable resources like corn starch, PLA straws offer transparency and mechanical properties similar to conventional plastic. They are compostable under industrial conditions, making them a popular choice where such facilities are accessible. PLA straws are designed for cold beverages and perform well without sogginess.
- PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) Straws: Considered a breakthrough, PHA straws are derived from renewable plant sources (e.g., cornstarch, sugarcane). They are home and industrial compostable, and critically, marine degradable in as little as 90-180 days, offering a significantly reduced environmental footprint even in marine environments. PHA straws offer high durability and a feel remarkably close to traditional plastic, making them ideal for a premium customer experience across various beverage types.
- قش قصب السكر: Made from bagasse, the fibrous byproduct of sugarcane processing, these straws are an excellent upcycled choice. They are 100% home compostable, PLA/BPA/PFAS-free, and exceptionally sturdy for both hot and cold beverages, providing a reliable and pleasant user experience without dissolving.
- Agave Straws: Upcycled from agave fibers, a byproduct of tequila and agave syrup production, agave straws are durable in hot and cold drinks and do not get soggy. They are biodegradable and designed to decompose within 12 months, with 95% degradation in just 6 months in landfills, and leave no microplastics. They are non-toxic and offer a strong sustainability narrative.
C. Natural Fiber Straws: Wheat, Reed, Bamboo
For a more rustic or natural aesthetic, fiber-based straws offer fully biodegradable and compostable options derived directly from plants.
- Wheat Stalk Straws: An ingenious use of agricultural byproduct, these straws are 100% natural, plastic-free, PFAS-free, sturdy, and zero-waste. They hold up well in both hot and cold beverages, providing a natural and eco-conscious choice.
- Reed Plant Stems: Organic, water-resistant, and durable for both hot and cold beverages, reed straws are compostable in soil and marine environments, making them an environmentally robust option.
- قش الخيزران: Natural, rapidly renewable, and requiring minimal resources to grow, bamboo straws are 100% biodegradable and compostable, offering high environmental friendliness. While reusable bamboo straws can withstand 10-20 uses, careful ethical sourcing is crucial to avoid issues like monoculture that can undermine their sustainability credentials.
D. Innovative & Edible Options for Unique Experiences
Beyond the primary categories, innovative edible and novel material straws provide unique customer experiences and absolute zero-waste solutions.
- قش المعكرونة: Edible and compostable, these straws can even be flavored, offering a completely zero-waste solution that adds an interactive element to beverages.
- Seaweed Straws: Easy to grow, carbon-absorbing, and with a texture surprisingly similar to plastic, seaweed straws biodegrade rapidly into marine animal food, offering an exceptional marine-friendly profile.
- Rice Straws: Completely biodegradable, often gluten-free, and edible, rice straws are suitable for various beverages and provide a truly circular solution if consumed or allowed to degrade naturally.
Edible straws are inherently safe, non-toxic, and naturally degrade if not consumed, significantly reducing environmental burden and offering a compelling story for eco-conscious brands.
E. Comparison Table: Key Eco-Friendly Straws for B2B Procurement
| ميزة | التأثير التشغيلي B2B | ملاحظة الامتثال | إمكانات العائد على الاستثمار |
|---|---|---|---|
| القش الورق | Widely available, familiar to staff. Earlier versions prone to sogginess; modern ones improved. | Generally biodegradable/compostable; crucial to check for PFAS-free certification. | Lower initial cost than some alternatives, meets basic plastic ban compliance. Risk of customer dissatisfaction if quality is poor; improved quality can reduce complaints and boost brand image. |
| قش قصب السكر | Sturdy for hot/cold beverages, offers good user experience. Minimal sogginess. | 100% home compostable, PLA/BPA/PFAS-freecertifications commonly available. | Enhanced brand image and strong sustainability narrative. May be slightly pricier than basic paper, but robust performance reduces customer complaints and potential for waste stream cost reduction if composted properly. Appeals strongly to eco-conscious consumers willing to pay a premium. |
| القش PHA | High durability and performance, closely resembling traditional plastic feel, suitable for diverse beverage types. | Home & industrial compostable, marine degradable (90-180 days). Strong future-proofing against stricter regulations. | Premium user experience justifies higher cost. Positions brand as cutting-edge in sustainability. Significantly positive environmental impact for brand story and consumer engagement. Strong compliance with evolving regulations, reducing long-term risk. |
| Agave Straws | Durable in hot/cold beverages, designed to prevent sogginess. Consistent performance. | Biodegradeswithin 12 months (95% in 6 months in landfill)without microplastics. | Upcycled material enhances sustainability narrative, resonating with environmentally aware customers. Good performance minimizes customer service issues. While initial cost might be higher, the strong eco-credentials can attract and retain a valuable customer segment, leading to increased revenue and reduced waste disposal costs over time. |
| Reusable Straws (Metal/Glass) | Requires significant washing/sanitization infrastructure, robust inventory management, and loss prevention strategies. High labor for cleaning. | No disposal compliance concerns if reused; ensures long-term plastic avoidance. | High upfront cost for inventory and specialized dishwashing equipment/labor. Long-term cost savings on disposables; strong sustainability statement for dine-in. However, operational complexities and potential for loss/breakage can reduce overall efficiency and ROI unless strategically focused on specific dine-in only applications. Not practical for high-volume takeout. |
Choosing the right eco-friendly straw material balances performance, compliance, and cost for your restaurant.
III. Strategic Bulk Sourcing of Eco-Friendly Straws: Best Practices
Successful transition to eco-friendly straws hinges on a strategic approach to bulk procurement, focusing on supplier reliability, robust certifications, and cost-effectiveness.

A. Identifying Reputable Bulk Suppliers for Eco-Friendly Straws
Partnering with the right suppliers is paramount for consistent quality and supply. Prioritize suppliers specializing in sustainable foodservice products, such asServous, WebstaurantStore, Good Start Packaging, and Holy City Straw Company. These companies often have expertise in eco-friendly materials and compliance.
A practical first step is to inquire with your current food service supplier about their eco-friendly straw options; for example,US Foods’ “Serve Good®” portfoliooften includes such alternatives. Look for companies offeringwholesale pricing, free samples, and volume discountsfor large orders to manage costs effectively. For businesses with higher volume needs or specific customization requirements, consider direct wholesale manufacturers likePanda Bambu, which may offer custom orders and larger Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), sometimes requiring30-50 cartonsfor certain products. For more detailed regulatory information,consult our comprehensive guide on sustainable packaging regulations.
B. Certifications and Quality Assurance for Sustainable Sourcing
Due diligence in sustainable sourcing is critical. Always verify certifications to ensure genuine eco-friendliness and compliance. Look for certifications likeBiodegradable Products Institute (BPI), Compost Manufacturing Alliance (CMA), or TÜV AUSTRIAfor industrial and/or home compostability standards. These certifications ensure that products will break down as claimed under specific conditions.
Furthermore, ensure products are explicitly labeled as100% plant-based, PLA-free, BPA-free, and PFAS-freefor genuine eco-friendliness and safety. SeekFDA approvalfor materials that come into contact with food, andFSC® Certifiedlabels for sustainably sourced paper products. Before committing to large orders, always request samples to test durability in various beverages (hot, cold, smoothies) and confirm no off-taste or undesirable characteristics.
C. Cost-Effectiveness and ROI of Eco-Friendly Straws
While the initial cost per eco-friendly straw may behigher than conventional plasticcounterparts, strategic bulk purchasing significantly mitigates this difference. Beyond unit cost, the return on investment (ROI) extends to avoiding potential regulatory fines and attracting a growing segment of higher-spending, eco-conscious customers.
Research indicates that switching to eco-friendly options can lead to long-term savings through improved brand perception and increased customer loyalty. For reusable options, studies show thatreusable plastic dishes need 10-17 usesto be more sustainable than single-use alternatives, demonstrating a break-even point and long-term ROI potential from disposables. For smaller businesses, considercollaborative purchasing initiativeswith other local restaurants or businesses to leverage larger volume discounts and collectively reduce costs. Explore more ROI insights in ourdeep dive into sustainable packaging ROI.
D. Mini Case Study: Cava’s Holistic Sustainability Impact
Mediterranean fast-casual chainCavaexemplifies a comprehensive and impactful approach to sustainable sourcing and operations, demonstrating that sustainability extends far beyond just straws. Cava actively publishes an Impact Report detailing its efforts across its supply chain and operations.
Notably, Cava partnered withToo Good To Go, a food waste reduction initiative, redirecting an estimated77,360 meals in the past yearto minimize food waste and support communities. This initiative directly addresses food security while reducing environmental burden. Furthermore, Cava collaborates withRubiconto enhance its composting and recycling services, ensuring that sustainable packaging and food waste are properly diverted from landfills. This integrated approach not only boosts Cava’s brand image and resonates with its customer base but also drives operational efficiencies by reducing waste disposal costs and optimizing resource utilization.
Strategic bulk sourcing and verified certifications are key to successful eco-friendly straw implementation.
IV. Overcoming Operational Challenges & Maximizing Impact
Implementing eco-friendly straws isn’t just a procurement decision; it requires strategic operational adjustments and clear communication to maximize its positive impact and ensure a seamless customer experience.

A. Addressing Durability and Customer Experience with Eco-Friendly Straws
The transition to eco-friendly straws requires careful consideration of material durability to maintain customer satisfaction. Choose straw materials based on the specific beverage type and expected duration of use. For instance,sugarcane or PHA strawsare robust choices for hot drinks or prolonged use in cold beverages, with PHA straws designed to decompose rapidly, inas little as 90 days in soil.
Communicate the benefits of the chosen material to customers, setting appropriate expectations for performance (e.g., politely explaining that paper straws may soften slightly over extended periods). Offer a variety of sizes, from cocktail to standard, smoothie, and boba colossal sizes, to ensure the appropriate fit and performance for all menu items.Expert opinion highlights durable plant-based straws (PHA, sugarcane, agave) as crucialfor a positive customer experience, as they closely resemble the performance characteristics of traditional plastic.
B. Navigating Disposal and Composting Complexities
Proper disposal is critical for realizing the environmental benefits of compostable straws. Procurement managers must understand local composting infrastructure; many compostable straws, particularly PLA, requireindustrial composting facilitieswhich may not be readily available in all regions. Without access to such facilities, compostable products may end up in landfills, where they behave similarly to conventional plastics.
To guide customers and staff, clearly label disposal bins and packaging. Educate staff thoroughly on the importance of separating compostable items, as even20% improper disposal can significantly undermine environmental benefits. Regulations, such as those in San Francisco, explicitlyprohibit compostable plastic straws if littered, emphasizing the need for proper facility access and diligent waste stream management.
C. Staff Training and Communication for Sustainable Initiatives
A successful sustainability initiative requires comprehensive staff buy-in and effective communication. Train employees on the environmental benefits of eco-friendly straws, their proper handling, and correct disposal protocols. Empower staff to articulate the restaurant’s commitment to sustainability to guests, building a shared narrative and reinforcing brand values.
Implement a“straws upon request” policyto significantly reduce overall straw consumption byapproximately 30%, leading to considerable resource and cost savings. Integrate sustainability training into new employee onboarding and conduct regular refreshers to ensure ongoing adherence and awareness. This proactive approach not only optimizes your eco-friendly straw program but also positions your staff as knowledgeable ambassadors for your brand’s sustainability mission. For more on staff training, see ourguide to sustainable operations training.
Effective operational adjustments and clear communication maximize the positive impact of eco-friendly straws.
V. Future Trends & Innovation
The landscape of sustainable foodservice is continually evolving, driven by innovation in materials, processes, and regulatory foresight. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for long-term competitive advantage.
The broader compostable packaging market is projected to reach$121.38 billion by 2025, indicating a widespread shift and increasing availability of innovative alternatives beyond straws. The bioplastics market, a key component of this shift, is experiencing robust growth, estimated to reachUSD 42.37 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 14.10% from 2025 to 2034. This expansion is driven by policy pressure, stronger corporate sustainability targets, and improving feedstock flexibility, leading to more diverse and high-performing materials.
Future trends over the next 5-10 years will likely see:
- Next-Generation Bioplastics: Continued development of advanced bioplastics like PHA that offer superior performance (heat resistance, durability) and enhanced degradability (e.g., marine biodegradability), moving closer to truly circular solutions.
- Upcycled Agricultural Waste: Increased utilization of agricultural byproducts and waste streams (e.g., coconut leaves, rice husks, mango peels) to create novel, fully biodegradable materials for straws and other disposables, reducing both waste and reliance on virgin resources.
- Edible Packaging Expansion: Growth in diverse edible straw options and broader edible packaging, offering true zero-waste solutions that can be consumed or naturally degrade into the environment if uneaten.
- Smart Packaging Integration: Evolution towards “smart packaging” that incorporates sensors or indicators for food safety and freshness, while simultaneously being compostable or highly recyclable.
- Enhanced Certification & Traceability: More stringent and globally harmonized certification standards for compostability and biodegradability, alongside advanced supply chain traceability (e.g., leveraging blockchain) to verify sustainability claims from source to disposal.
- Reusable Systems Scaling: Increased adoption and refinement of reusable container and cutlery programs, especially for dine-in and loyalty programs, driven by both environmental goals and long-term cost savings.
- PFAS-Free Mandates: Stricter regulations and consumer demand for PFAS-free coatings in all food contact materials, pushing manufacturers toward safer and truly non-toxic solutions.
- Carbon Footprint Optimization: Greater focus on Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) to evaluate the full environmental impact of materials, including production and transport, driving innovation towards materials with the lowest overall carbon footprint.
These innovations will provide foodservice businesses with an even wider array of effective, compliant, and environmentally superior options, enabling a more profound commitment to sustainability.
Future trends in sustainable foodservice promise innovative materials and enhanced compliance for restaurants.
VI. Competitive Advantage & Business Case
Embracing eco-friendly straws and broader sustainable sourcing is not merely a cost center; it is a powerful strategic investment that delivers tangible competitive advantages and a compelling business case for B2B decision-makers.
Quantifiable benefits include:
- Cost Savings & Risk Mitigation: Proactive adoption of eco-friendly straws helps restaurants avoid punitive fines associated with plastic straw bans. While initial unit costs may be higher, bulk purchasing and reduced overall consumption through “straws upon request” policies can lead to significant savings. Furthermore, integrating sustainable practices across the supply chain, while potentially incurring higher upfront costs for “green” materials, yields long-term savings by optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and mitigating future regulatory risks. For example, reusable dishes, though requiring high upfront investment, surpass the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of single-use items after just 10-17 uses.
- Enhanced Brand Value & Customer Loyalty: With 80% of consumers preferring eco-friendly products, a visible commitment to sustainability directly translates to an uplift in brand perception. Restaurants that prioritize environmental responsibility attract and retain a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, who are often willing to pay a premium for sustainable options. This leads to increased foot traffic, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth marketing, building a stronger, more resilient brand.
- Market Share Opportunity: The global eco-friendly straw market’s projected growth to $25.1 billion by 2035 signals a vast and expanding market segment. By aligning with this trend, restaurants can capture a larger share of environmentally-minded diners and differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace. Early adopters gain a significant first-mover advantage, establishing themselves as leaders in sustainable practices.
- Operational Efficiency & Waste Reduction: Beyond straws, a holistic sustainable sourcing strategy (e.g., local sourcing, food waste reduction programs like Cava’s partnership with Too Good To Go, comprehensive recycling and composting initiatives) can significantly reduce operational waste and its associated costs. This extends to optimizing energy and water use within the restaurant, further contributing to the bottom line.
In essence, integrating eco-friendly straws and sustainable sourcing into your restaurant’s core operations is a strategic imperative that translates environmental responsibility into quantifiable economic and reputational gains. It’s an investment in your brand’s future resilience and market leadership.
Sustainable sourcing offers restaurants significant competitive advantages and a strong business case.
خاتمة
The transition to eco-friendly straws is a strategic necessity for modern restaurants, driven by pervasive market demand (projectedeco-friendly straw market growth to $25.1 billion by 2035) and critical regulatory shifts (EU plastic baneffective July 2021). By understanding the diverse material options, prioritizing certified bulk suppliers, and embracing a holistic approach to sustainability across your operations, your restaurant can not only navigate this shift successfully but also significantly enhance its brand reputation, attract a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers, and contribute meaningfully to environmental preservation. Proactive engagement with sustainable sourcing safeguards your operations, secures your market position, and demonstrates undeniable leadership in a rapidly evolving industry.
Take action now to transform your restaurant’s environmental impact and elevate your brand’s commitment to sustainability. Request a tailored bulk sample pack of certified eco-friendly straws to see the quality and compliance benefits firsthand.






