La industria mundial de servicios de alimentos se encuentra en una coyuntura crítica, enfrentando una presión sin precedentes para adoptar la sostenibilidad. Con Las ventas orgánicas en EE. UU. alcanzarán un estimado de $52 mil millones de dólares en 2021, lo que representa el 5,5 % de todas las ventas minoristas de alimentos., la demanda de los consumidores de opciones ambientalmente responsables no es solo una tendencia: es un imperativo estratégico. Este cambio se ve amplificado por la cruda realidad de que La producción de alimentos por sí sola aporta aproximadamente el 25% de las emisiones mundiales de gases de efecto invernadero (GEI)., lo que obliga tanto a los consumidores como a las instituciones a exigir prácticas más ecológicas.
Para los gerentes de adquisiciones, directores de operaciones, funcionarios de sostenibilidad y ejecutivos de la cadena de suministro, ignorar este cambio sísmico conlleva importantes riesgos operativos y comerciales. El incumplimiento de las cambiantes regulaciones ambientales, el creciente escrutinio de los consumidores y el impacto tangible del cambio climático en las cadenas de suministro plantean amenazas directas a la rentabilidad y la relevancia del mercado. Por el contrario, los mayoristas están en una posición única para ser los ejes de esta transición, uniendo a los productores con conciencia ecológica con una base de clientes de servicios de alimentos en rápida expansión. Al incorporar proactivamente la sostenibilidad en sus operaciones principales, los mayoristas no sólo pueden cumplir con las expectativas éticas de los compradores, sino también desbloquear una ventaja competitiva crucial, mejorar la reputación de la marca y atraer nuevos clientes de alto valor en un mercado saturado.
Abastecimiento estratégico: cultivar una cartera de productos más ecológica para el mercado de servicios alimentarios ecológicos
Acceder al mercado de servicios de alimentación ecológicos comienza con una estrategia de abastecimiento sólida y transparente. Esto implica una selección meticulosa de productos que cumplen con rigurosos estándares ambientales y éticos, abordando directamente la creciente demanda de alimentos sostenibles y trazables.
Prioritizing Certified & Local Products for Market Credibility
Generar confianza y validar afirmaciones ecológicas requiere un compromiso con productos certificados. Asociarse con productores que se adhieren a certificaciones de terceros reconocidas como USDA Orgánico, el Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) para productos pesqueros sostenibles, o el Comercio Justo para productos de origen ético proporcionan pruebas verificables de responsabilidad ambiental y social. Estas certificaciones no son meras etiquetas; son garantías de que los productos cumplen con estándares estrictos desde la granja hasta la mesa, lo que permite a sus clientes de servicios de alimentos comercializar con confianza sus ofertas sustentables entre sus propios clientes.
Más allá de las certificaciones, enfatizar el abastecimiento local es un poderoso diferenciador. Distribuidores como El Mercado Común, una organización sin fines de lucro, conecta con éxito más de 300 granjas familiares sostenibles con instituciones como escuelas, hospitales y universidades.. Este modelo no solo reduce la huella de carbono asociada con el transporte de larga distancia, sino que también respalda las economías locales y garantiza ingredientes más frescos. Como consumidores en 2025 prefiere cada vez más entender el origen y la sostenibilidad de sus alimentos, garantizar la transparencia y la trazabilidad de la cadena de suministro se vuelve primordial. Esto le permite generar confianza con los clientes de servicios de alimentos al brindarles información detallada sobre los orígenes de los productos, las prácticas agrícolas y los datos de impacto ambiental.
Diversificar categorías de productos sostenibles para lograr un atractivo más amplio
Una cartera integral ecológica se extiende más allá de los productos orgánicos. Los mayoristas deben ofrecer una selección diversa de productos que aborden diversas facetas de la sostenibilidad, desde alternativas vegetales hasta envases innovadores.
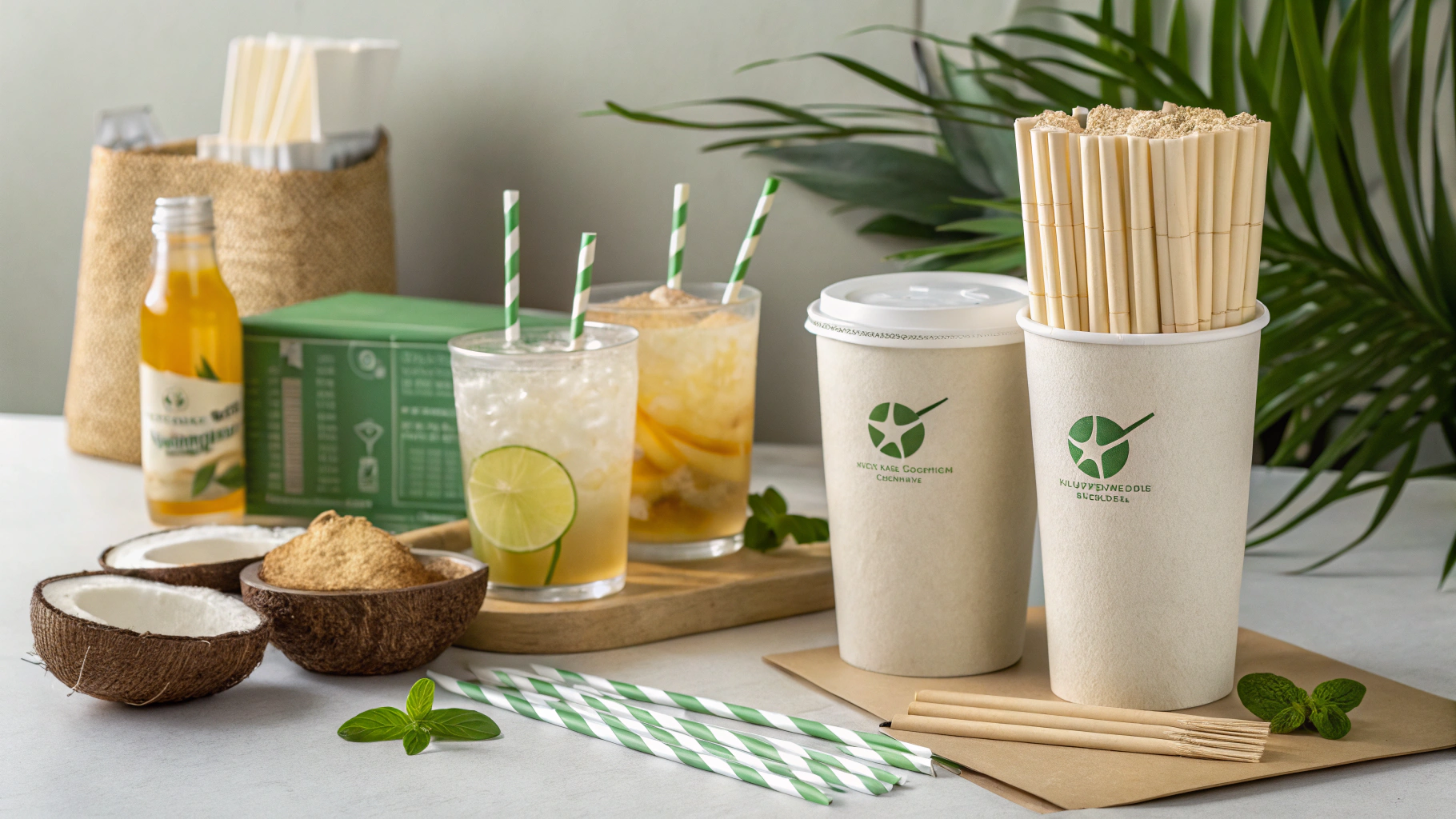
Seleccione una amplia variedad de productos frescos, naturales, orgánicos y especiales de calidad para alinearse con las expectativas éticas del comprador. Esto incluye expandirse hacia Alimentos funcionales, de origen vegetal y fuentes de proteínas alternativas., lo que refleja el crecimiento significativo de las dietas “flexitaristas” y el interés de los consumidores por la salud y la sostenibilidad. Por ejemplo, el Se espera que el interés en proteínas alternativas y de origen vegetal continúe en 2025., presentando una importante oportunidad de mercado.
Además, un área crítica de diversificación son los envases sostenibles para el sector alimentario. Ofrezca una selección completa de artículos compostables, reciclados y reutilizables, incluidas marcas populares como GreenStripe® products made from renewable plant materials and BlueStripe™ products from post-consumer recycled content, both offered by Eco-Products. Innovate with sustainable packaging solutions, such as those made from Ingeo biobased materials, which reduce reliance on traditional plastics and align with growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly packaging. Providing alternatives like eco-friendly straws for restaurants can significantly help your clients meet their own sustainability goals and comply with evolving single-use plastic regulations.

Operationalizing Sustainability: Transforming Wholesaler Logistics with Green Logistics
Strategic sourcing must be complemented by sustainable operational practices. Green logistics, which focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of supply chain activities, is no longer a niche concept but a core component of competitive wholesale distribution.
Optimizing Energy & Fleet Efficiency for Reduced Carbon Footprint
The operational footprint of a wholesale business—from warehousing to delivery—offers substantial opportunities for carbon reduction and cost savings.
Investing in energy-efficient warehousing is a foundational step. Implement solutions such as LED lighting, smart HVAC systems, electric roller shutter doors with sensors, plastic curtains, and evaporative coolers. These technologies significantly minimize energy consumption for cooling and lighting, reducing overall CO2 emissions. For example, installing solar panels to power warehouses can drastically reduce reliance on fossil fuels, aligning with global sustainability goals like those set by major corporations.
Transitioning delivery fleets is another high-impact area. Moving towards electric vehicles (EVs) or biodiesel vans can significantly reduce tailpipe emissions and greenhouse gas output. For refrigerated transport, consider utilizing motorless refrigeration units on trucks and painting refrigerated vehicles white to reflect sunlight, thereby reducing cooling energy requirements. Route optimization software, leveraging AI and IoT, can further reduce fuel consumption and vehicle miles, leading to 10-20% fuel cost savings and lower maintenance. This efficient transportation and temperature control is critical for high-volume, short-shelf-life food products, reducing both environmental impact and operational costs.
Minimizing Waste Across the Supply Chain Through Sustainable Distribution
Food waste is a pressing global issue, with approximately 30-50% of produced food being wasted across the supply chain. Wholesalers have a pivotal role in mitigating this.
Adopt efficient inventory management and advanced demand forecasting using technology. Accurate data analytics can significantly reduce excess inventory and minimize food waste, helping clients prevent overstocking and spoilage. Beyond prevention, implementing composting and surplus food donation programs diverts edible food from landfills. Resources like the EPA’s Reducing Wasted Food & Packaging Toolkit provide invaluable guidance for commercial and institutional food services on tracking and reducing waste through improved stocking, handling practices, and staff training.
Prioritize recyclable, compostable, and biodegradable packaging solutions for all distributed products. This decreases reliance on landfill-bound plastic and aligns with evolving single-use plastic bans and waste diversion goals. Furthermore, utilize technology for continuous monitoring of storage conditions at wholesale stages to reduce food loss and waste, especially crucial for sensitive, short-shelf-life products.
| Característica | Impacto operativo B2B | Nota de cumplimiento | Potencial de retorno de la inversión |
|---|---|---|---|
| Route Optimization | Reduced fuel consumption, fewer vehicle miles. | Aligns with emissions reduction targets (e.g., EU Green Deal). | 10-20% fuel cost savings, lower maintenance. |
| Electric Fleet Transition | Reduced tailpipe emissions, quieter operations. | Future-proofs against tightening emission regulations. | Long-term fuel savings, potential tax incentives. |
| Smart Warehouse Management | Minimized energy use for cooling/lighting, optimized space. | Supports ISO 14001 certification for environmental management. | 15-25% energy cost reduction, improved stock rotation. |
| Compostable Packaging Adoption | Reduced landfill waste, enhanced client appeal. | Meets evolving single-use plastic bans and waste diversion goals. | Reduced waste disposal costs, increased market share. |
Building Bridges: Collaborative Partnerships in the Eco-Friendly Foodservice Market
No single entity can transform the foodservice industry alone. Wholesalers thrive by fostering robust collaborative partnerships across the entire value chain, from farm to fork.
Connecting Farms to Fork: Fostering Regional Food Systems
True sustainability in foodservice distribution requires building strong, resilient regional food systems. Mini Case Study: A prime example of this is The Common Market, a non-profit regional wholesale food distributor. They have successfully established direct connections between over 300 sustainable family farms and large institutional markets like schools, hospitals, and universities. By aggregating products from multiple local farms, The Common Market ensures the volume and consistency needed to supply larger clients, overcoming a common barrier for individual small farms. This model keeps food dollars within communities, fostering new business opportunities and strengthening local economies. Similarly, Paragon Foods demonstrates effective collaboration by connecting local farmers directly to restaurant chains like Eat’n Park, ensuring a consistent supply of sustainable produce.
These partnerships provide an essential blueprint for wholesalers: actively seeking out and nurturing relationships with local, sustainable producers. This not only reduces transportation emissions but also provides fresh, high-quality ingredients that appeal to a discerning, eco-conscious market.

Leveraging Industry Standards & Initiatives for Collaborative Impact
Beyond individual partnerships, engaging with broader industry initiatives and standards solidifies a wholesaler’s commitment to sustainability and demonstrates leadership.
Actively engage with industry-wide initiatives such as the Courtauld Commitment 2030 in the UK, which aims to reduce food waste, water usage, and greenhouse gas emissions across the food and drink supply chain. Participating in or aligning with frameworks like the Food Waste Reduction Roadmap demonstrates a commitment to collective action and industry-wide improvement.
Promote and prioritize products that carry recognized certifications, such as BPI certified compostable products. These certifications, often backed by industry associations or standards bodies, assure clients of a product’s environmental integrity and enhance your credibility and market position. Collaborate with all your suppliers to deliver on shared commitments to sustainability across the entire supply chain. This holistic approach ensures that environmental stewardship is embedded throughout the product lifecycle, from cultivation to delivery. Supporting farmers in economically and environmentally sustainable production through strong, equitable relationships ensures a consistent supply of high-quality, green products.
Empowering Clients: Education, Transparency, & Technology for Sustainable Distribution
Your role as a wholesaler in the eco-friendly foodservice market extends beyond just supplying products; it involves empowering your clients to embrace and leverage sustainability themselves.
Educating Foodservice Partners on Green Benefits
Many foodservice operators are keen to go green but may lack the knowledge or resources. Position your company as a valuable partner by providing detailed information on product origins, certifications, and environmental impact data for eco-friendly items. This transparency builds trust and enables your clients to confidently communicate their sustainable choices to their own customers.
Offer training and resources to clients on integrating sustainable ingredients into their menus and effectively marketing these green choices. Demonstrate the long-term cost savings associated with eco-friendly practices, such as reduced waste disposal fees and enhanced customer loyalty stemming from a strong environmental image. For instance, explaining the lifecycle and benefits of tiempos de descomposición de la paja compostable can educate clients on tangible environmental impacts. Help them understand how a commitment to sustainable practices can meet their corporate environmental goals and resonate with their increasingly eco-conscious diners.
Harnessing Digital Innovation for Supply Chain Transparency & Green Logistics
The future of sustainable foodservice distribution is inextricably linked to technological advancement. Leveraging digital tools offers unparalleled opportunities for efficiency and transparency.
Harness AI and IoT for accurate demand forecasting, improved stock control, and real-time emissions tracking. Academic research in green logistics highlights how these technologies provide deeper insights into the supply chain, helping identify inefficiencies and optimize energy use. Utilizing integrated digital platforms not only allows you to reach a larger customer base but also significantly enhances traceability from farm to fork.
Smart food supply chain platforms can centralize dispersed data, optimizing logistics and ensuring a stable and sustainable food supply. This translates into improved supply chain efficiency, reducing the time between production and delivery for fresher ingredients and less waste. By embracing these innovations, you can offer clients not just products, but a pathway to a more transparent, efficient, and environmentally responsible operation.
The ROI of Green: Tangible Benefits for Wholesalers in the Eco-Friendly Foodservice Market
Embracing the eco-friendly foodservice market is not just an ethical choice; it’s a shrewd business strategy with quantifiable returns on investment. Wholesalers who lead with sustainability gain a distinct competitive edge that translates into significant financial and reputational gains.
Cost Savings & Competitive Advantage: Achieve significant cost reductions through relentless pursuit of energy efficiency, waste minimization, and optimized transportation. Reduced utility bills from energy-efficient warehouses, lower waste disposal fees, and optimized fuel consumption from smart logistics directly impact your bottom line. This operational efficiency provides a tangible competitive edge, allowing you to offer competitive pricing while maintaining healthy margins.
Reputación de marca mejorada: In an era where consumers are increasingly factoring environmental impact into their purchasing decisions, demonstrating a verifiable commitment to environmental stewardship is a powerful brand builder. This attracts new, ethically aligned clients and significantly enhances customer loyalty among existing ones. A strong reputation as a sustainable wholesaler differentiates you in a crowded market and builds goodwill.
Increased Resilience: Building a sustainable supply chain inherently improves business resilience. By diversifying sourcing, optimizing resource use, and reducing waste, you become less vulnerable to supply chain disruptions, resource scarcity, and price volatility. Proactively addressing environmental factors prepares your business for future market shifts and enhances long-term stability.
Cumplimiento de Normatividad: The regulatory landscape surrounding environmental practices is continually evolving, particularly in the US and EU. By proactively meeting evolving environmental regulations and policies—such as single-use plastic bans or emissions reduction targets—you avoid potential penalties, fines, and reputational damage. Adopting sustainable practices positions you as a forward-thinking leader, fostering a positive public image and ensuring long-term market access.
Conclusión
The eco-friendly foodservice market is not merely a trend but a transformative force reshaping the industry’s future. Wholesalers who strategically embrace sustainable sourcing, green logistics, collaborative partnerships, and digital innovation are positioned for significant growth and long-term success. By leading with purpose, you can unlock new revenue streams, strengthen your brand, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Act now: Partner with eco-conscious suppliers and optimize your operations to capture your share of the rapidly expanding eco-friendly foodservice market. The time to build a resilient, responsible, and profitable wholesale enterprise is today.






