The global push for corporate sustainability has reached a critical juncture, compelling businesses to meticulously examine every facet of their operational footprint. For procurement managers, operations directors, and sustainability officers in thehospitality & foodservice industries, single-use plastics represent a particularly high-stakes challenge. Americans alone consume an estimated 500 million straws daily (National Park Service, 2018), with conventional plastic versions persisting in landfills and oceans for centuries, breaking down into harmful microplastics. This environmental burden not only poses ecological threats but also significant operational and commercial risks, including escalating regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and misaligned consumer expectations (UNEP, 2023; European Commission, 2019).
Understanding the precise decomposition times of compostable straws is no longer merely an environmental aspiration; it is a critical imperative for informed procurement, regulatory compliance, and strategic risk mitigation. This comprehensive guide provides data-backed insights, empowering B2B decision-makers to navigate the complexities of sustainable sourcing and ensure their investments deliver tangible environmental and commercial returns.
Informed procurement of compostable straws is crucial for hospitality and foodservice to mitigate risks and achieve sustainability goals.
How Long Do Compostable Straws Take to Decompose? Understanding the Variability
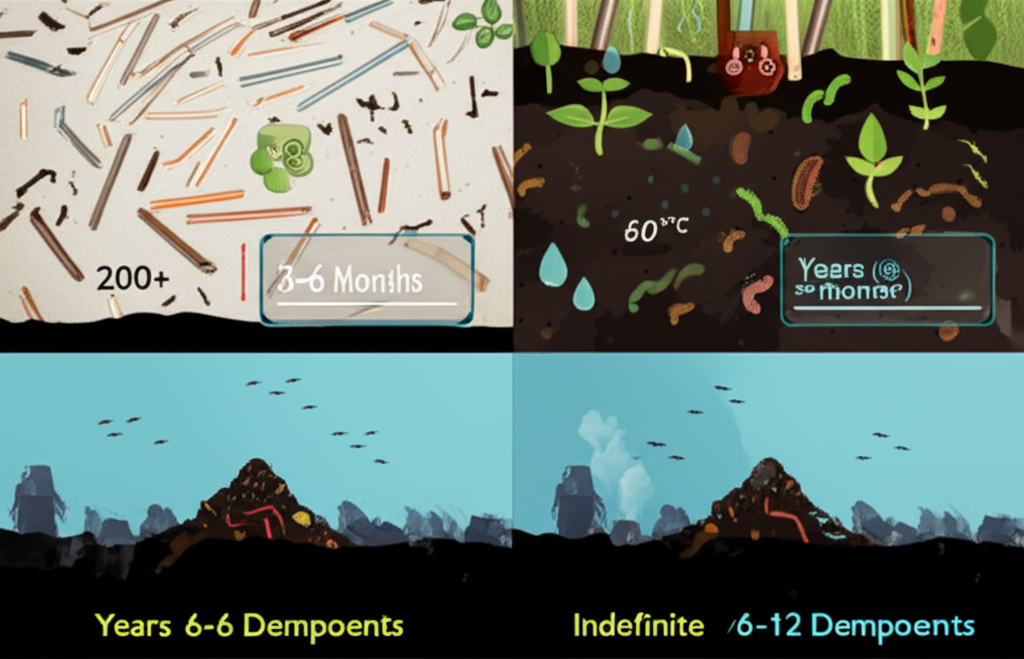
The promise of compostable straws lies in their ability to break down into natural components such as water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. However, the exact decomposition time is highly variable, ranging from a few weeks to over a year, depending significantly on the material composition and the specific composting environment. In stark contrast, traditional petroleum-based plastic straws can endure for 200 years or more, fragmenting into persistent microplastics that infiltrate ecosystems and food chains.
This variability underscores a crucial distinction: not all “compostable” products perform identically in all disposal scenarios. While some materials offer rapid degradation in highly controlled conditions, others require specific industrial infrastructure to fulfill their environmental promise.
Compostable straw decomposition times vary significantly based on material and composting environment.
Industrial Composting: The Optimal Pathway for Compostable Straw Decomposition
For most compostable straws, industrial composting facilities represent the optimal environment for rapid and complete degradation. These facilities are engineered to provide ideal conditions: sustained high temperatures (typically around 60°C or 140°F), meticulously controlled moisture levels, and a dense, active microbial population. Under these precisely managed parameters, the vast majority of industrially compostable straws are designed to break down within90 to 180 days (3 to 6 months).
Rigorous standards govern this process. For instance, the ASTM D6400 specification, a cornerstone for industrial compostability in North America, mandates that products achieve 90% biodegradation within six months and demonstrate 90% disintegration (meaning 90% of the material passes through a 2mm sieve) within 12 weeks. Similarly, the European standard EN 13432, commonly referenced for European markets, requires full compost formation within 180 days under industrial conditions.

Industrial composting facilities provide ideal conditions for compostable straws to break down within 3 to 6 months.
Leading Certifications and Standards for Compostable Straws
Navigating the landscape of compostable products requires adherence to globally recognized certifications that verify decomposition claims. These standards offer a critical layer of assurance for B2B purchasers seeking compliant and genuinely sustainable solutions.
- BPI Certified Compostable: In the United States, products bearing the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) certification mark meet rigorous U.S. standards, ensuring that they will biodegrade completely in industrial composting facilities without leaving harmful residues.
- TÜV AUSTRIA’s “OK compost INDUSTRIAL”: This widely respected European certification adheres to the EN 13432 standard, requiring full compost formation in 180 days within specialized industrial composting conditions. TÜV AUSTRIA also offers “OK compost HOME” for products suitable for home composting environments.
- Other Key Global Standards: Businesses operating internationally should also be aware of DIN-CERTCO (Germany/EU), AS 5810 (Australia), and NF T57-800 (France), which similarly validate compostability against stringent criteria. Prioritizing products with these certifications is paramount for ensuring regulatory compliance and avoiding greenwashing accusations.
Globally recognized certifications like BPI and TÜV AUSTRIA verify compostable product claims, ensuring compliance and sustainability.
Beyond Industrial Facilities: Compostable Straws’ Decomposition in Other Environments
While industrial composting offers the most reliable pathway, it’s crucial for operations and sustainability leaders to understand the fate of compostable straws in alternative disposal scenarios.
- Home Composting Realities: Products certified with “OK compost HOME” are designed to break down in less rigorous home composting conditions, typically within one year. However, many compostable straws on the market require the higher temperatures and controlled environments unique to industrial facilities. Without proper home composting conditions, these materials may persist much longer.
- Marine & Landfill Fate: Despite being designed for composting, some bioplastic and paper straws inevitably find their way into natural environments. A January 2024 study published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering found that certain commercial bioplastic or paper straws could disintegrate within 8 to 20 months in coastal ocean systems. However, this is significantly slower than industrial composting, and the extent of “disintegration” doesn’t always equate to full biodegradation into harmless components. In marine environments, bioplastic straws made of foam were found to break down at least twice as fast as solid versions. In contrast, the study noted that polypropylene (PP) and polylactic acid (PLA) straws showed no measurable weight changes after 16 weeks in ocean experiments, indicating long-term persistence.
- Landfill Challenges: Landfills, characterized by anaerobic (low-oxygen) conditions, are not conducive to the efficient decomposition of most compostable materials. Even certified compostable products break down very slowly in landfills, and this process can unfortunately generate methane gas—a potent greenhouse gas—rather than the inert biomass produced in aerobic composting. This highlights the importance of proper end-of-life infrastructure for true environmental benefit.

Compostable straws decompose slowly in home compost, marine, and landfill environments, emphasizing industrial composting’s importance.
Deep Dive: Decomposition Times by Compostable Straw Material
The material science behind compostable straws directly dictates their decomposition characteristics, functionality, and suitability for various B2B applications inhôtellerie et restauration.
- Paper Straws: Quick Breakdown, Functional Considerations
- Decomposition: Traditional paper straws can decompose in 2-6 weeks in optimal composting environments, aligning with data from the UK Environment Agency. More advanced, 100% biodegradable paper straws, showcased in a November 2022 Advanced Science study, achieved complete decomposition after 120 days, with over 50% weight loss in just 60 days. This significantly outperforms conventional paper straws (which showed only 5% weight loss in the same study). These advanced paper straws even demonstrated good decomposition in marine environments (e.g., coastal South Korea at 1.5-2m depth), overcoming typical challenges like low temperature and high salinity.
- Functional Considerations: While cost-effective and widely available, conventional paper straws are often criticized for becoming soggy, impacting the customer experience. Newer generations address this with improved coatings and material science.
- Sugarcane (Bagasse) Straws: Robust & Rapidly Degrading
- Decomposition: Sugarcane (bagasse) straws are highly efficient, often decomposing within approximately 90 days under optimal industrial composting conditions. Those certified as home compostable can break down in a home compost bin in less than 2 months or within 360 days, demonstrating remarkable versatility.
- Functional Considerations: Known for their durability and natural feel, bagasse straws are less prone to sogginess than many paper alternatives and offer good heat resistance, making them ideal for cafes and restaurants.
- PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) Straws: Versatile Biodegradation
- Decomposition: PHA straws are a promising bioplastic, derived from fermented plant sugars, capable of breaking down within 15 months in coastal ocean environments. Crucially, they are noted for their compostability in both home and industrial settings. Studies have shown some breakdown in seawater within 6 months, a notable advantage over PLA or some paper straws in marine conditions.
- Functional Considerations: PHA straws offer a plastic-like durability and feel, providing a premium experience suitable for high-end hotels or airlines. Their versatile disposal options make them attractive for businesses serving diverse customer bases.
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) Straws: Industrial Composting Imperative
- Decomposition: PLA straws, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, are a common compostable material. They typically break down within 90-180 days in industrial composting facilities operating at temperatures of 56-60°C.
- Functional Considerations: PLA straws effectively mimic the functionality and feel of traditional plastic straws, making them a popular choice for various foodservice operations. However, it is critical to understand that research indicates little to no significant degradation in soil or natural water environments over periods as long as 120 days. Without specific industrial conditions, PLA can take years to break down, potentially contributing to landfill burden.
Different compostable straw materials offer varied decomposition rates and functional properties for B2B applications.
Comparative Analysis of Compostable Straw Materials
Choosing the right compostable straw material requires a strategic evaluation of operational impact, compliance, and return on investment forhospitality and foodservice businesses.
| Fonctionnalité | Impact opérationnel B2B | Note de conformité | Potentiel de retour sur investissement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pailles en papier | Widely available, often cost-effective; newer versions mitigate sogginess; ideal for quick-service. | Check for “100% biodegradable” certifications (e.g., Advanced Science study) for optimal performance. | High initial adoption, meets basic eco-mandates; lower perceived quality for some but improving. |
| Canne à sucre (Bagasse) | Durable, heat-resistant, natural feel; moderate cost; good for extended use in cafes and bars. | Often home and industrial compostable; verify specific certifications like “OK compost HOME.” | Enhanced customer experience, strong sustainability alignment, reduced waste. |
| Pailles PHA | Premium plastic-like durability, versatile disposal options; suitable for diverse venues, including hotels. | Certified for industrial, home, and marine degradation; supports broader environmental claims. | Premium branding, broader end-of-life solutions, minimizes waste liability; higher initial cost. |
| Pailles PLA | Mimics plastic functionality; widely sourced; suitable where industrial composting is accessible, like large catering operations. | Strictly requires industrial composting (ASTM D6400, EN 13432).Misdirection risks. | Cost-effective for operations with robust access to industrial composting infrastructure; risk of landfill accumulation without proper disposal. |
Selecting compostable straw materials requires balancing operational needs, compliance, and ROI for hospitality businesses.
Strategic Implications for B2B: Compliance & Sustainability ROI
Adopting verified compostable straw solutions is more than a conscientious choice; it’s a strategic business decision that drives competitive advantage and long-term value forhospitality and foodservice procurement managers.
- Navigating Regulatory Landscapes: Proactive adoption of certified compostable products helps businesses meet the increasing wave of single-use plastic bans and sustainability mandates globally. Aligning with standards like EN 13432 and ASTM D6400 is essential for market access and avoiding non-compliance penalties, especially in regions like the EU that are aggressively phasing out problematic plastics. Staying ahead of these regulations provides a significant competitive edge. For a detailed overview of global regulations, consult our guide on global plastic straw regulations.
- Enhancing Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty: Demonstrating a verifiable commitment to environmental stewardship through truly compostable products resonates powerfully with eco-conscious consumers and B2B clients alike. The market for eco-friendly straws is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach nearly USD 25.1 billion by 2035, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.3%. Businesses that lead this transition stand to capture significant market share and build enduring customer loyalty. This commitment also positively impacts ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) scores, attracting investors and talent.
- Operational Efficiency & Waste Management: Implementing proper disposal infrastructure for certified compostable products reduces landfill waste volumes and can lead to lower waste disposal costs in the long run. This aligns with circular economy principles, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible, reducing reliance on virgin resources and minimizing environmental impact. For organizations with on-site composting or access to industrial facilities, this translates to tangible operational savings and a verifiable reduction in environmental footprint. For further guidance on selecting the right partner, consider consulting a guide on how to choose a compostable straw distributor.
Adopting certified compostable straws offers hospitality businesses regulatory compliance, enhanced reputation, and operational efficiencies.
Case Study: Breakthroughs in Paper Straw Decomposition Rates
The perception of paper straws as easily soggy and slow to decompose is rapidly changing thanks to advancements in material science. A groundbreaking November 2022 study published inAdvanced Scienceshowcased the development of100% biodegradable paper strawsthat significantly outperform conventional alternatives.
These innovative straws achieved complete decomposition after120 daysin controlled decomposition tests, a dramatic improvement over traditional paper straws that only showed 5% weight loss over the same period. More impressively, they demonstratedover 50% weight loss in just 60 days, signaling rapid degradation. Even when tested in challenging marine environments—submerged at a depth of 1.5–2 meters on the coast of South Korea—these new paper straws showed good decomposition, defying the typical hindrances of low temperature and high salinity. This research highlights the ongoing innovation in sustainable materials, offering businesses more robust and truly eco-friendly paper straw options for theirfoodservice operations.
New paper straw technologies demonstrate rapid decomposition, even in marine environments, improving their viability for foodservice.
Future Trends & Innovation
The landscape of compostable materials is evolving rapidly, driven by regulatory pressures, consumer demand, and scientific breakthroughs. Over the next 5-10 years, we can expect several key trends impactinghospitality and foodservice supply chains:
- Advanced Bioplastics: Further development of materials like PHA and potentially new polymers that offer enhanced functionality, broader end-of-life options (e.g., marine biodegradability), and improved cost-effectiveness. Research into foamed cellulose diacetate (CDA), for instance, shows promise for straws that degrade significantly faster than solid versions in seawater while retaining desirable plastic-like properties.
- Enhanced Paper Technologies: Continued innovation in paper-based solutions, focusing on improved durability, liquid resistance, and faster decomposition rates across diverse environments, as demonstrated by the Advanced Science study.
- Novel Plant-Based Materials: Exploration of entirely new bio-based materials, such as bacterial cellulose (BC) enhanced with other components, which have shown complete decomposition in soil within as little as 20 days in some studies, far outperforming current PLA-based options.
- Harmonized Global Standards: Increased efforts to standardize and clarify “compostable” and “biodegradable” labeling globally, reducing confusion and preventing greenwashing. This will simplify procurement for international businesses.
- Intégration de l’économie circulaire : Greater emphasis on designing products for closed-loop systems, where compostable items are collected, processed, and returned as valuable soil amendments, truly embodying circularity. This will necessitate significant investment in composting infrastructure worldwide.
- Smart Packaging: Integration of technologies that can track a product’s end-of-life journey, providing transparency and optimizing collection for composting facilities.
Future trends in compostable straws include advanced bioplastics, enhanced paper, novel plant-based materials, and harmonized global standards.
Conclusion: Driving Sustainable Operations with Verified Compostable Solutions
The transition from conventional single-use plastics to truly compostable alternatives is a strategic imperative for modern businesses. By meticulously understanding the verified decomposition times and required conditions for diverse materials—including advanced paper, robust sugarcane, versatile PHA, and industrially reliant PLA—procurement managers, operations directors, and sustainability executives can make informed decisions that resonate across their entire value chain within thehospitality and foodservice sectors.
Prioritizing certified products that align with available disposal infrastructure ensures that your sustainability investments yield tangible environmental benefits and meet increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. This strategic pivot not only mitigates compliance risks and enhances brand reputation but also contributes to a more sustainable and efficient operational model. For a more comprehensive overview, refer tothe ultimate B2B guide to compostable straws.
Understanding compostable straw decomposition is vital for hospitality businesses to achieve sustainability, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Ready to Transform Your Operations?
Act now to audit your current single-use plastics and transition to certified compostable straws that truly decompose, elevating your environmental stewardship and securing your market position in a rapidly evolving, eco-conscious economy.Contact Us for a Sustainable Solution
Foire aux questions (FAQ)
Q: How long do compostable straws take to decompose in industrial facilities?►
A: Most industrially compostable straws are designed to break down within 90 to 180 days (3 to 6 months) under the controlled high temperatures, moisture levels, and microbial activity found in industrial composting facilities. This is verified by standards like ASTM D6400 and EN 13432.
Q: Can compostable straws decompose in home composting bins?►
A: Only products specifically certified “OK compost HOME” are designed to break down in less rigorous home composting conditions, typically within one year. Many compostable straws on the market require the higher temperatures and controlled environments unique to industrial facilities and will not fully decompose in a typical home compost bin.
Q: What happens to compostable straws if they end up in landfills or oceans?►
A: In landfills, which are anaerobic (low-oxygen), most compostable materials break down very slowly and can produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas. In marine environments, some bioplastics may disintegrate over 8 to 20 months, but full biodegradation into harmless components is significantly slower than industrial composting, and some materials like PLA show little to no degradation.
Q: How can hospitality businesses ensure proper disposal of compostable straws?►
A: Hospitality businesses should partner with local industrial composting facilities to establish collection programs. Clearly labeling waste bins for compostable items and educating staff and customers on proper waste separation are crucial steps to ensure these straws reach the correct end-of-life infrastructure and fulfill their environmental promise.
Q: Are sugarcane straws truly compostable and durable enough for busy foodservice environments?►
A: Yes, sugarcane (bagasse) straws are highly efficient, often decomposing within approximately 90 days under optimal industrial composting conditions. They are also known for their durability, natural feel, and good heat resistance, making them an excellent and reliable choice for high-volume foodservice operations like cafes, restaurants, and event catering.
Illustration Prompt 1:An illustration depicting a cross-section of an industrial composting facility, showing high temperatures, moisture, and microbes breaking down organic waste, with a compostable straw visibly transforming into soil. Focus on the controlled environment.
Illustration Prompt 2:An illustration showing different disposal paths for compostable straws: one going into a home compost bin (with slower decomposition), one floating in a calm ocean (showing partial disintegration), and one buried in a landfill (showing minimal change). Emphasize the varied outcomes.
Illustration Prompt 3:A comparative illustration of different compostable straw materials (paper, sugarcane, PHA, PLA) with small icons or visual cues representing their key characteristics like durability, heat resistance, and decomposition speed. Use a clean, infographic style.
Illustration Prompt 4:An illustration of a procurement manager, operations director, and sustainability officer collaboratively reviewing data on a tablet, with a background showing a modern, eco-friendly hotel or restaurant. The image should convey strategic decision-making and positive environmental impact.
“






