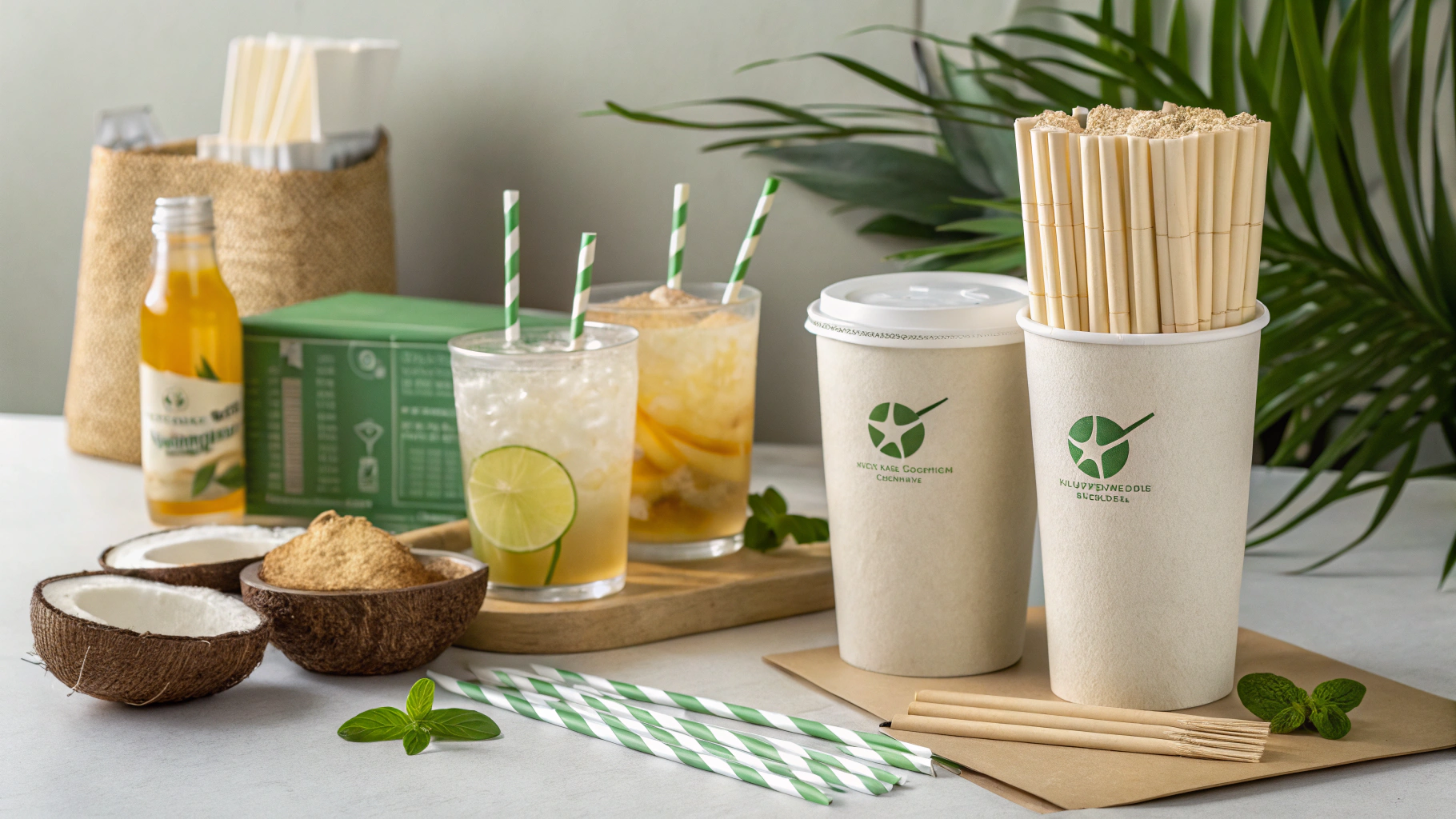
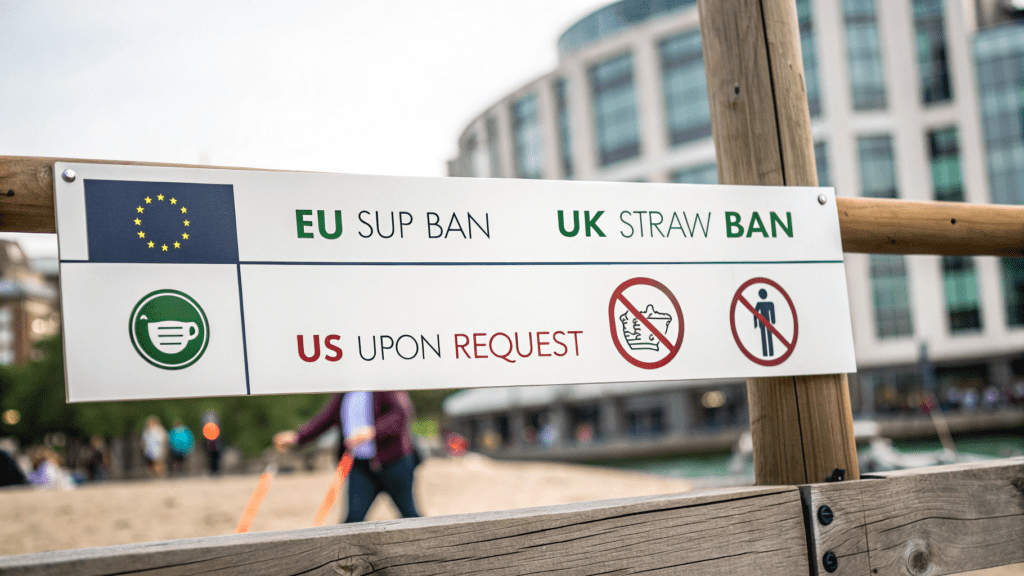
The global conversation around environmental stewardship has reached a critical inflection point, placing unprecedented pressure on businesses to rethink every aspect of their operations. For procurement managers, operations directors, sustainability officers, and supply chain executives, the seemingly small decision of a drinking straw now carries significant weight, impacting brand reputation, compliance, and ultimately, profitability. The days of ubiquitous single-use plastic straws are rapidly receding, driven by a powerful wave of regulatory action and evolving consumer expectations. Remember the viral 2015 video of a plastic straw removed from a sea turtle’s nostril? That pivotal moment galvanized a movement, highlighting that these small plastic tubes, taking up to 200 years to decompose, are significant contributors to ocean pollution. Businesses ignoring this shift risk not only public backlash but also a direct hit to their bottom line through fines, decreased customer loyalty, and a tarnished brand image in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Navigating this transition, however, is far from straightforward. The initial wave of eco-friendly, non-bendable straw alternatives introduced its own set of operational pitfalls and customer experience challenges. Many first-generation paper straws quickly became soggy, disintegrated prematurely, or imparted an unpleasant taste, leading to widespread consumer dissatisfaction. Stainless steel straws, while durable, often carry a metallic taste or become uncomfortably hot with certain beverages. More critically, the shift has ignited a significant controversy around accessibility. For millions of individuals with disabilities, chronic illnesses, or mobility issues, the flexibility, softness, and disposability of traditional plastic straws are not merely conveniences but necessities for safe and independent hydration. Rigid alternatives like metal, glass, or bamboo can pose severe injury risks, including chipped teeth or lacerations, especially for those with tremors or involuntary movements—a tragic incident involving a metal straw even resulted in a fatality. Paper and pasta straws, when degrading, can become choking hazards. This “eco-ableism” critique underscores the complex balance between environmental goals and inclusive customer service, creating a major compliance and ethical dilemma for procurement teams. Furthermore, the environmental impact of some alternatives isn’t always clear-cut. While plant-based PLA straws offer a plastic-like feel, they often require commercial composting facilities to break down effectively, facilities that are not universally available, leading to these alternatives still ending up in landfills. The energy and water consumption during the production of certain alternatives also raise questions about their true lifecycle carbon footprint compared to plastic. As Europe emerges as an innovation hub for next-generation eco-friendly solutions and US consumer preferences, especially among millennials and Gen Z, rapidly shift towards plant-based options, understanding these nuances is paramount for strategic decision-making.
The good news is that the industry is rapidly evolving, driven by material science breakthroughs and a commitment to addressing these complexities. Innovations are leading to next-generation non-bendable straw solutions that deliver on both performance and sustainability. Research engineers are developing paper straws with advanced food-grade coatings from agricultural crop residue, enhancing durability and preventing sogginess, while other innovations explore biodegradable plastic coatings like polybutylene succinate (PBS) with cellulose nanocrystals to improve resilience and ocean biodegradability. Beyond paper, the market is seeing a surge in plant-based polymers like PLA and other novel materials derived from agave fibers, hay, sugarcane, pasta, and even dried-up coconut leaves. These materials often provide a more pleasant user experience while reducing environmental impact. When considering reusable options, manufacturers are refining designs for stainless steel, glass, and silicone, focusing on ergonomic improvements and ease of cleaning for high-volume, multi-use environments, reducing the overall total cost of ownership in the long run. Even bamboo, a long-standing sustainable material, is seeing innovation with solutions likebendable bamboo fiber strawsemerging to address flexibility needs while maintaining eco-credentials.

B2B Comparison Guide for Non-Bendable Straw Materials
To navigate this diverse landscape, a strategic sourcing and selection process is crucial. Decision-makers need to evaluate materials not just on cost, but on performance, safety, and alignment with their operational infrastructure and brand values.
| Fonctionnalité | B2B Impact | Compliance Risk | Potentiel de retour sur investissement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pailles en papier | Widely available, brandable, single-use convenience. | Varies based on coatings; potential for customer dissatisfaction. | Low initial cost, high brand alignment with sustainability; risk of high reorder rates. |
| Pailles PLA | Plastic-like feel, single-use, derived from renewable resources. | Requires specific industrial composting infrastructure, not widely available. | Depends on local composting; reduced landfill fees if properly disposed; higher unit cost. |
| Pailles en bambou | Natural aesthetic, reusable, compostable (if untreated). | Inconsistent quality can lead to splinters; hygiene for reuse. | Good for premium branding; high cleaning costs for reusable;innovations like bendable bamboo fiber strawsenhance utility. |
| Acier inoxydable | Highly durable, premium feel, reusable for high-end service. | Injury risk for vulnerable populations; temperature conductivity. | High upfront cost offset by longevity; reduced waste management costs. |
| Paies de verre | Elegant, taste-neutral, reusable. | Fragile; high injury risk; requires careful handling. | High upfront cost; reduced waste; suitable for controlled, high-end environments. |
| Pailles comestibles | Zero waste, novel customer experience, marketing appeal. | Degrades in liquid, alters taste; potential choking hazard. | High unit cost; strong brand differentiator; limited beverage compatibility. |
Leading national chains like Starbucks and McDonald’s are already setting precedents. In December 2024, Starbucks began offering Green Planet™ straws in Japan, demonstrating a tangible commitment to innovative, eco-friendly alternatives. Such transitions are not just about compliance; they are about securing market share and aligning with conscious consumer spending. The global eco-friendly straws market is projected for significant growth, from an estimated USD 12.3 billion in 2025 to nearly USD 25.1 billion by 2035, growing at a robust CAGR of 7.3%. This growth is fueled by government regulations, such as increasing bans on single-use plastics, and the widespread adoption of “straws on request” policies, which strike a pragmatic balance between environmental goals and accessibility needs.

Technological advancements are also transforming the production landscape. AI-powered systems are being deployed to optimize manufacturing processes for eco-friendly straws, from precise material selection to molding, significantly reducing waste and increasing efficiency. Companies like Corn Next, which introduced non-toxic, biodegradable straws made from cornstarch in July 2025, and Teknor Apex, which expanded its bioplastics offerings by acquiring Danimer Scientific in June 2025, exemplify the industry’s rapid innovation. North America is anticipated to lead the global eco-friendly market with 30.0% of total revenue in 2025, with the USA alone projected for a 7.5% CAGR from 2025 to 2035, while Europe remains a crucial hub for developing next-generation solutions. As innovations continue, with a focus on creating durable, cost-effective, and flexible biodegradable straws, the future promises a wider array of sustainable choices. For example, advancements in processing agricultural waste into durable, single-use products, akin tobendable bamboo fiber strawsthat offer both sustainability and functionality, are poised to reshape the market. This ongoing material exploration is vital.

Charting a future-proof course for your organization’s straw program requires a methodical approach. Begin with a comprehensive internal audit to assess your specific operational needs, customer demographics, and existing waste management infrastructure. This will illuminate the most viable material options and identify potential accessibility gaps. Next, pilot new materials in controlled environments, gathering actionable feedback from both staff and customers. This iterative process allows for informed adjustments before large-scale adoption, mitigating risks of widespread dissatisfaction. Develop clear, transparent communication strategies, internally and externally, to educate consumers about your sustainability initiatives and demonstrate your commitment to inclusivity by explaining “straws on request” policies. Partnering with innovative and reliable suppliers, like those highlighted in the industry insights, who are committed to quality, consistency, and ongoing R&D in sustainable materials, is also paramount.
Leading the way in responsible beverage service means moving beyond mere compliance. It demands a strategic, informed, and inclusive approach to non-bendable straws that not only protects our planet but also safeguards your brand and serves all your customers. Embrace innovation now to mitigate risk, realize substantial cost savings through efficient procurement and waste reduction, and amplify your brand’s value proposition. Secure your market share by proactively adopting a sustainable straw strategy that positions your enterprise as a forward-thinking leader in an evolving global economy.
Questions fréquemment posées
What are the primary drivers for adopting non-bendable straws in B2B?
The primary drivers include escalating pressure for eco-friendly operations, global regulatory shifts away from single-use plastics, corporate social responsibility goals, and evolving consumer expectations. Adopting sustainable non-bendable straws enhances brand reputation, ensures compliance, and drives competitive advantage.
What are the main challenges associated with early eco-friendly straw alternatives?
Early alternatives often suffered from operational pitfalls like soggy paper, metallic taste, or premature degradation. A significant challenge is ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities, as rigid materials can pose injury risks. There are also hidden environmental costs, such as the need for specific commercial composting for PLA straws and the overall carbon footprint of production.
How do non-bendable straws impact accessibility for individuals with disabilities?
Many individuals with disabilities rely on the flexibility and softness of traditional plastic straws for safe and independent drinking. Rigid non-bendable alternatives like metal, glass, or hard bamboo can pose serious injury risks (e.g., chipped teeth, lacerations) for those with tremors or involuntary movements, leading to “eco-ableism” concerns. Some businesses adopt “straws on request” policies to balance environmental goals with accessibility.
What are the key materials used in next-generation non-bendable straws?
Next-generation non-bendable straws leverage advanced materials like durable paper with innovative coatings, plant-based polymers (e.g., PLA, agave, hay, sugarcane, pasta), and materials derived from agricultural waste like coconut leaves. Refined reusable options include stainless steel, glass, and silicone, with ongoing innovations in flexibility like bendable bamboo fiber straws.
What is the projected market growth for eco-friendly straws?
The global eco-friendly straws market is projected for significant growth, estimated to reach around USD 12.3 billion in 2025 and nearly USD 25.1 billion by 2035, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.3%. North America is expected to lead this market, with Europe acting as a key innovation hub.






