Maree mutevoli: perché le cannucce di plastica monouso non sono più sostenibili per le aziende
Il panorama delle imprese, in particolare nei settori dinamici della ristorazione e dell’ospitalità, sta subendo una profonda trasformazione. Quella che una volta era una comodità onnipresente – la cannuccia di plastica monouso – è ora un problema significativo. I governi di tutto il mondo stanno intensificando i divieti e le restrizioni sulla plastica monouso, comprese le cannucce, con importanti direttive dell’Unione Europea e varie azioni legislative in numerosi stati degli Stati Uniti. Questo contesto normativo in continua evoluzione richiede un perno fondamentale per le imprese: l’adozione di alternative sostenibili non è più solo un’aspirazione ambientale ma un requisito fondamentale per la conformità e la continuità operativa.
Questo imperativo svela anche un’enorme opportunità di mercato. Si prevede che il mercato globale delle cannucce ecologiche, valutato a circa 12,3 miliardi di dollari nel 2025, quasi raddoppierà fino a raggiungere i 25,1 miliardi di dollari entro il 2035, dimostrando un robusto tasso di crescita annuale composto (CAGR) del 7,3%. Questa significativa traiettoria di crescita segnala chiaramente un cambiamento definitivo del mercato e un’ottima opportunità per i primi utilizzatori di assicurarsi la leadership di mercato e un vantaggio competitivo. Al di là della semplice conformità, l’adozione di soluzioni di paglia sostenibili aumenta direttamente la reputazione del marchio e favorisce la fiducia dei consumatori. Dato che circa l'80% dei consumatori preferisce attivamente prodotti ecologici, il passaggio alle cannucce naturali è un percorso diretto per migliorare l'immagine del marchio, attirando un segmento crescente di consumatori attenti all'ambiente e differenziando la tua attività in un mercato affollato.

Dall'inquinamento al progresso: l'imperativo per le soluzioni con paglia naturale
Il costo reale delle cannucce di plastica va ben oltre il prezzo di acquisto iniziale. Questi articoli monouso, realizzati principalmente in polipropilene (PP), un sottoprodotto del petrolio, rappresentano un grave onere ambientale. Non sono biodegradabili, persistono per oltre 200 anni e si scompongono in un pervasivo inquinamento microplastico che si infiltra nel nostro suolo, nell’acqua e persino negli ecosistemi marini. Il danno devastante alla vita marina, che spesso ingerisce questi frammenti, si traduce in significativi rischi aziendali: pubbliche relazioni negative, potenziali sanzioni normative e diminuzione della fedeltà dei consumatori in una società sempre più eco-consapevole.
Yet, the concept of a natural drinking tube is far from new. Our current transition back to sustainable materials is, in many ways, a sophisticated evolution of historical practices. Tracing the roots of drinking straws reveals ancient Mesopotamians and East Asians utilizing hollow reeds and bamboo for sipping beverages around 3000 BCE. The 19th century saw the widespread use of rye grass straws, though these had their own limitations, often imparting an undesirable grassy flavor or quickly disintegrating. It was Marvin Stone’s 1888 innovation of the paper straw that marked a significant step towards a manufactured, yet still plant-based, solution. Today, this historical lineage culminates in a modern re-embrace of plant-based solutions, driven by technological advancements and ecological urgency. For a deeper dive into sustainable business practices, explore howmomoio.com/sustainability-solutionspuò aiutare.
Il variegato mondo delle cannucce ecologiche mette ora in mostra un ampio spettro di materiali naturali e sostenibili all'avanguardia dell'innovazione. Ciò include carta avanzata (in particolare kraft vergine, apprezzata per la sua purezza e resistenza), bambù durevole, acido polilattico (PLA) derivato da amidi vegetali e opzioni riutilizzabili di metallo e vetro. Inoltre, stanno entrando nel mercato alternative vegetali all’avanguardia come riso, alghe, amido di mais, pasta e grano, che offrono proprietà uniche come la commestibilità. I continui sforzi di ricerca e sviluppo sono fortemente concentrati sul miglioramento della durabilità, sul miglioramento della resistenza all'acqua attraverso rivestimenti avanzati (come le opzioni senza PFAS) e sulla riduzione dei costi di produzione per soddisfare le esigenti esigenze B2B, garantendo una qualità senza compromessi.
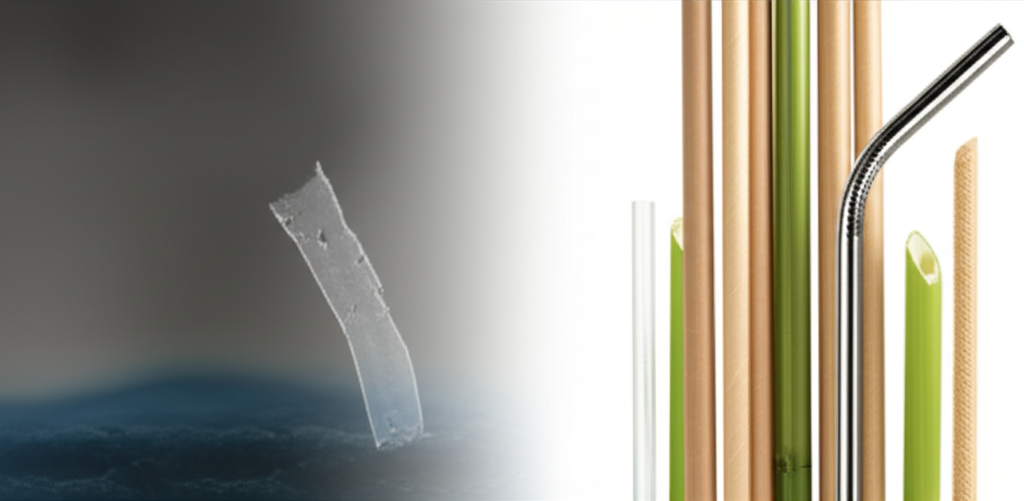

Vantaggi strategici: perché i materiali naturali hanno prestazioni migliori per il tuo business
Embracing natural straw solutions offers significant strategic advantages, moving beyond mere compliance to foster true operational excellence and supply chain resiliency. Diversifying your straw supply chain with multiple natural material options reduces reliance on single-source traditional plastics, mitigating supply disruptions and price volatility that have become increasingly common. Furthermore, the long-term operational benefits include reduced waste management costs, simpler adherence to increasingly complex environmental regulations, and a clear pathway to a more circular economy. For streamlined B2B sourcing of eco-friendly products, consider platforms likemomoio.com/b2b-sourcing.
Choosing the right sustainable straw for your business requires a nuanced understanding of the available options. Here’s a comparative analysis of leading natural straw materials, outlining their specific B2B advantages, ideal use cases, and key considerations:
| Paper (Virgin Kraft) | High purity, superior strength, biodegradable. Excellent for QSRs, cafes. Market projected to reach USD 6.17 billion by 2030 (15.6% CAGR). | Watch for sogginess if not properly coated; check for PFAS-free certification. |
| Bambù | Reusable, natural aesthetic, lightweight, chemical-free. Preferred in strict anti-plastic regions (e.g., some EU countries). | Requires cleaning for reuse; can absorb liquid over extended use. Bamboo straw market to USD 320.1 million by 2035 (7.8% CAGR). |
| PLA (Plant-Based Bioplastic) | Compostable, resembles traditional plastic, suitable for wider diameters (smoothies, bubble tea). | Requires industrial composting facilities; can soften at high temperatures. Often accused of “greenwashing” if not properly disposed of. |
| Sugarcane Bagasse | Sturdy, long-lasting, biodegradable. Made from upcycled waste fibers from sugarcane. | Relatively new to market; broader adoption is increasing. |
| Reusable (Stainless Steel/Glass) | Highly durable, long-term solution, non-toxic. Ideal for premium and eco-conscious establishments (e.g., high-end restaurants, hotels). | Requires washing and sanitation; can be dangerous if used while walking (metal/glass); potential temperature conductivity. |
| Rice/Pasta/Wheat Straws | Edible (rice/pasta), fully biodegradable, unique consumer experience. | Can alter taste slightly; prone to sogginess (pasta); higher cost; specific use cases. |
| PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoate) | Marine-biodegradable (decomposing in 58 days in controlled environments), resembles plastic, withstands high temps. FDA-approved. | Newer technology, potentially higher cost; supply chain still developing. |
Addressing common concerns associated with early natural straw versions, such as sogginess or taste alteration, is crucial. Modern innovations have largely overcome these hurdles. The availability of advanced solutions like PFAS-free paper straws and marine-biodegradable PHA straws ensures both consumer safety and a superior user experience. For businesses navigating these choices, expert guidance on sustainable packaging solutions, like those offered atmomoio.com/sustainable-packaging, can be invaluable.
Proactively adopting these sustainable alternatives positions your business as an industry leader. North America and Europe, driven by stringent regulations and high consumer awareness, are significant markets for these innovations. For example, the paper straw market alone is projected to reach USD 6.17 billion by 2030 (15.6% CAGR), and the bamboo straw market to USD 320.1 million by 2035 (7.8% CAGR). This forward-thinking approach not only attracts the growing eco-conscious customer base but can also lead to significant cost savings through reduced environmental footprints and avoidance of potential regulatory fines. To understand the latest regulatory shifts impacting your business, refer to the European Union’s Single-Use Plastics Directive atec.europa.eu. For market data and trends in eco-friendly products, reputable sources such asfuturemarketinsights.comoffer comprehensive insights.

Embrace the Future: Your Next Step Towards Sustainable Operations
The global pivot away from single-use plastics towards natural material straws is undeniable and accelerating. Governments, consumers, and businesses worldwide are recognizing the urgent need for change. Adapting to this irreversible shift is not just an option but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming for long-term relevance and competitive advantage in a sustainability-driven market. Those who delay risk falling behind.
The benefits of this transition are compelling and multifaceted: enhancing your brand image, ensuring regulatory compliance, optimizing operational efficiency by reducing waste and avoiding fines, and capturing a significant share of the rapidly growing eco-conscious market. Investing in natural materials is a critical step towards future-proofing your business and securing a more profitable, sustainable future. Stay informed on global plastic pollution efforts and solutions by visitingourworldindata.org.






