A B2B Guide for Procurement, Operations, and Sustainability Leaders in Hospitality & Foodservice

The global coffee industry, valued at over $400 billion, is at a critical juncture. Once an afterthought, the humble drinking straw has emerged as a high-stakes operational and compliance challenge for procurement managers, operations directors, and supply chain executives. As regulatory pressures intensify and consumer expectations for sustainability rise, the choice of coffee straw material is no longer a minor purchasing decision—it’s a strategic imperative shaping market access, brand reputation, and long-term profitability.
Single-use plastics, including traditional plastic straws, face aggressive global bans, exemplified by the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive, which has already eliminated plastic straws in member states. In the U.S., states like California (AB1276, effective June 1, 2022) mandate straws only upon request, while the Philippines’ EPR Act of 2022 holds manufacturers financially responsible for plastic packaging waste, including straws. Ignoring this evolving landscape means risking regulatory fines, incurring higher waste disposal costs, and alienating a rapidly growing segment of eco-conscious consumers. The global non-plastic drinking straw market alone is projected to surge from an estimated $9.84 billion in 2023 to a remarkable $17.55 billion by 2028, underscoring the urgent need for B2B decision-makers to align operations with these eco-conscious trends.
Choosing sustainable coffee straws is crucial for hospitality and foodservice to meet evolving regulations and consumer demands.
The Core: What are Coffee Straws Made Of? Exploring Key Materials
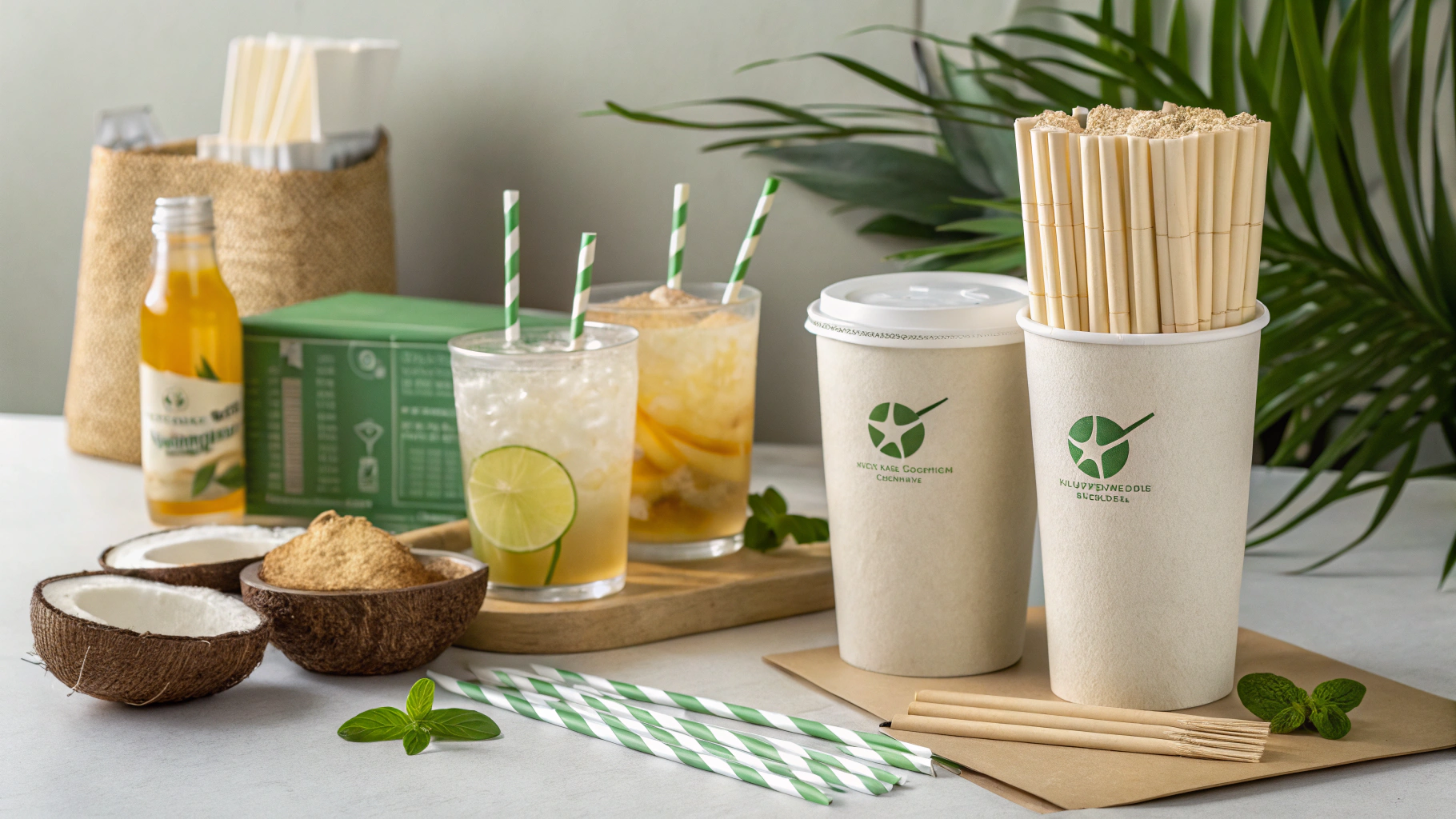
The days of a single, ubiquitous plastic straw are over. Today, the market offers a diverse array of innovative materials, each designed to meet specific performance, environmental, and commercial needs for both hot and cold beverages. Understanding these compositions is fundamental to making informed procurement decisions.
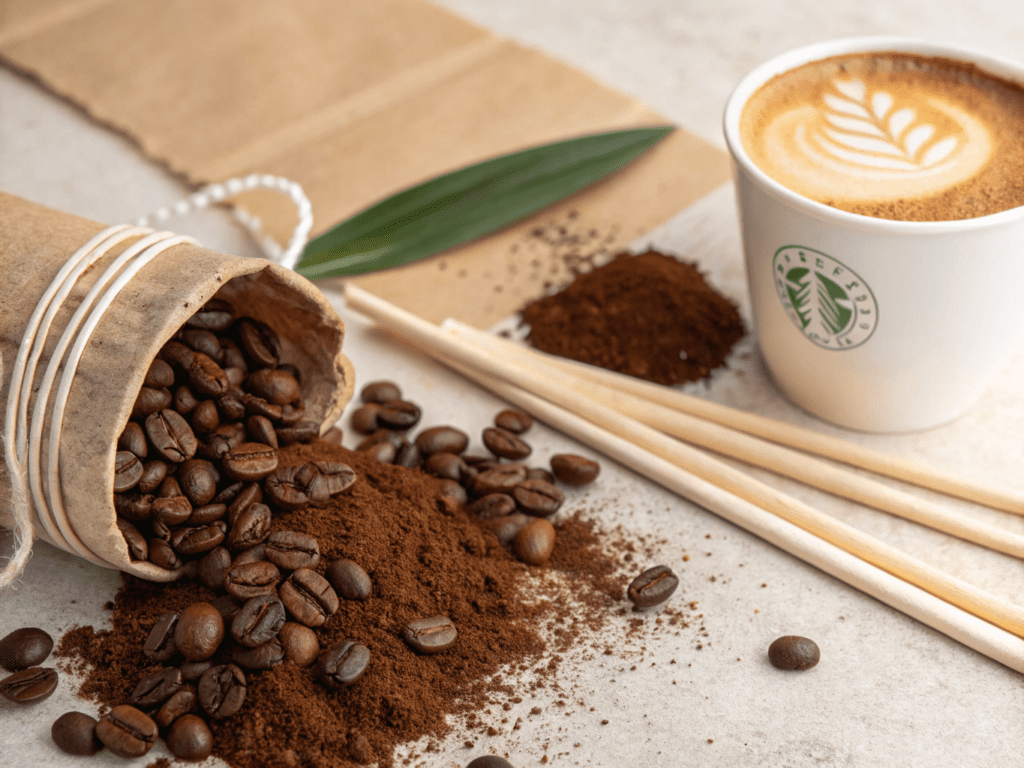
A. Innovative Coffee Grounds Straws: A Circular Economy Solution
One of the most compelling innovations in sustainable straws hails directly from the coffee industry itself: coffee grounds straws. These remarkable straws are crafted from recycled coffee grounds, a byproduct of coffee production, which are then combined with natural resins, plant-based fibers, and starches. This ingenious approach addresses two critical waste streams simultaneously: plastic pollution and the over 6 billion pounds of coffee waste generated globally each year.
The resulting material is 100% compostable and plastic-free, designed to break down naturally in industrial composting facilities within 90 to 180 days, or even in home and garden compost environments within 12-18 months. Beyond their impressive biodegradability, coffee grounds straws are engineered for performance. They offer remarkable durability and flexibility, mimicking the feel of traditional plastic straws without the environmental burden. Crucially for coffee establishments, they withstand temperatures up to 75°C (167°F) and are noted for not becoming soggy, a common pain point with earlier paper alternatives. They also carry a subtle, natural coffee aroma, enhancing the beverage experience without imparting any taste. Many are certified by the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) and comply with standards like ASTM D6400 and EN13432.
B. The Rise of Edible Coffee Straws: A Zero-Waste Indulgence
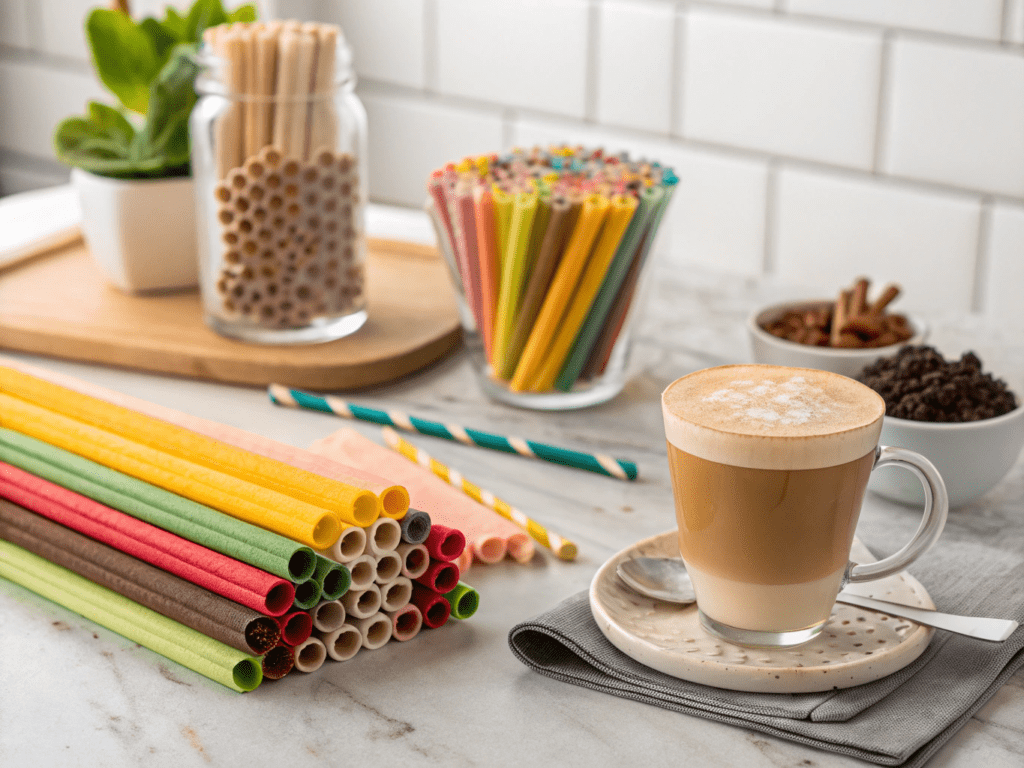

For businesses seeking to offer a truly zero-waste customer experience, edible coffee straws present an exciting frontier. These innovative straws are crafted from various plant-based materials such as repurposed coffee grounds, tapioca starch, rice flour, or other natural ingredients like sugar and corn starch. Brands like Sorbos and EQUO have pioneered edible straws that not only function as a drinking straw but can be consumed after use.
Edible straws are engineered for impressive structural integrity, maintaining their form for hours in cold drinks and up to an hour in hot beverages. They come in unflavored options that allow the coffee’s natural taste to shine through, or in various flavors like coffee, vanilla, or chocolate, offering a unique, indulgent, and truly zero-waste customer experience. Individually wrapped, they also address hygiene concerns for high-volume operations, boasting a shelf life of up to two years. The edible straws market is projected to reach USD 446.96 million in 2030, underscoring their growing appeal.
C. Plant-Based Biodegradable Straws: Sugarcane, PLA, and More
Beyond coffee grounds and edible varieties, a broad category of plant-based biodegradable straws offers diverse solutions:
- Sugarcane Straws (Bagasse): Made from bagasse, the fibrous byproduct of sugarcane processing, these straws are highly sustainable. They boast excellent heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 90°C (194°F), and are significantly more resistant to sogginess than traditional paper straws. They are 100% compostable, free from PLA and PFAS, and offer a robust, reliable option for hot coffee.
- PLA Straws (Polylactic Acid): Derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, PLA is a popular bioplastic due to its transparent, plastic-like feel. While industrially compostable, PLA straws can deform or soften above 60°C (140°F), making them less ideal for very hot coffee unless specifically formulated as heat-resistant (crystallized PLA, capable of withstanding up to 85°C). It’s crucial to note that PLA requires specific industrial composting facilities to break down, which may not be universally available.
- PHA Straws (Polyhydroxyalkanoate): Representing the next generation of biopolymers, PHA straws are produced by microorganisms and offer superior heat resistance, enhanced durability, and broad biodegradability in various environments, including marine water, soil, and composting facilities, without leaving microplastics.
- Other Natural Options: Materials like reed, grass, bamboo, and wheat straws also provide diverse applications. Bamboo and reed straws are highly durable and can often be reused. Grass straws are known for being chemical-free and decomposing naturally within six months.
D. Reusable Coffee Straws: Durability Meets Sustainability
For certain operational models, particularly those encouraging customers to bring their own cups, reusable coffee straws remain a highly sustainable choice. These are typically made from durable materials such as:
- Stainless Steel: Extremely durable and long-lasting for cold drinks, though they can conduct heat rapidly when used with hot beverages, potentially posing a burn risk.
- Glass (Borosilicate): Can withstand very high temperatures without imparting flavor, but are prone to breaking.
- Silicone: 100% BPA-free and highly flexible, silicone straws (e.g., KoffieStraw) are safe for hot drinks and are dishwasher-friendly, making them convenient for consumers. Google Trends data in July 2025 showed a sudden surge in “reusable coffee straw” searches, highlighting growing consumer interest in these long-term solutions.
While offering significant long-term waste reduction, reusable straws require a robust cleaning and sanitation infrastructure for B2B settings, and they still depend on customer adoption and commitment to regular washing.
Diverse sustainable straw materials offer varied performance and environmental benefits for B2B coffee operations.

Navigating the Market: Performance, Compliance, and Cost of Coffee Straws
For procurement managers and operations directors, selecting the right sustainable straw material involves a careful evaluation of performance, regulatory compliance, and economic viability.
A. Performance Benchmarks for Sustainable Coffee Straws: Beyond Soggy Paper
The early generation of paper straws, a common first step away from plastic, often became soggy within 20 minutes, severely compromising the customer experience and leading to dissatisfaction. This “soggy straw” dilemma highlighted the critical need for advanced materials.
Today’s innovative materials offer significant improvements:
- Advanced Materials: Sugarcane and coffee grounds straws, for instance, are engineered to maintain their integrity for hours, even in hot beverages, providing a consistent and enjoyable drinking experience.
- Heat Resistance is Crucial: Many standard plant-based straws, particularly earlier PLA versions, fail or deform above 60-90°C, making them unsuitable for hot coffee. Businesses must scrutinize heat resistance specifications to avoid functional failures and negative customer feedback. Materials like sugarcane and PHA are specifically designed to excel in high-temperature applications.
- Taste and Texture: Quality control is paramount. High-performance sustainable straws should be odorless and tasteless, ensuring they do not alter the delicate flavor profile of coffee. Their texture should also provide a comfortable, non-papery feel.
B. Regulatory Landscape & Compliance for Sustainable Straws: Navigating Global Bans
The global shift away from single-use plastics is not voluntary; it’s legally mandated in many key markets. Procurement strategies must prioritize compliance to mitigate significant risks.
- Global Plastic Bans: The EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD) already bans plastic straws, including PLA, in member states. This necessitates a complete pivot to genuinely plastic-free alternatives for European market access. The Philippines’ EPR Act of 2022 mandates increasing recovery targets for plastic packaging, including straws, reaching 50% in 2025 and 80% from 2028 onward, directly impacting manufacturers’ responsibilities.
- U.S. State Laws: In the U.S., states like California (AB1276) require straws only upon request, while New York City implemented similar rules in 2021. Businesses must be acutely aware of regional variations in plastic bans and “straws-upon-request” laws.
- PFAS Concerns: A growing concern surrounds “forever chemicals” (PFAS) detected in some paper and plant-based straws, used for water resistance. These chemicals can leach into hot beverages and pose significant health and compliance risks, leading to legal liabilities and reputational damage. Sourcing certified PFAS-free options is now a non-negotiable.
- Certifications: To ensure compliance and genuinely sustainable sourcing, B2B buyers must insist on verifiable certifications. Look for:
- BPI (Biodegradable Products Institute) Certification: Confirms industrial compostability in North America (meeting ASTM D6400/D6868 standards).
- EN13432: The European standard for industrial compostability.
- FDA Approval: Ensures food safety.
- Plastic-Free Verification: Essential for meeting most plastic ban regulations.
C. Economic Implications: ROI and Cost-Benefit for B2B Operations
While sustainable straws can have higher upfront costs—for example, PLA straws surged 67% in price in 2020, and paper straws can be significantly more expensive than plastic—the long-term ROI is compelling.
- Consumer Willingness to Pay: A significant 74% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable packaging, and adopting eco-friendly solutions can boost customer loyalty by up to 20%. This translates directly to increased revenue and stronger brand equity.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Shifting to compostable straws can reduce waste disposal fees by diverting materials from landfills. Furthermore, the enhanced brand image attracts environmentally conscious customers, expanding market share without heavy marketing spend.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Strategic bulk purchasing from specialized B2B platforms and direct manufacturers can help optimize costs. Procurement managers should evaluate total cost of ownership, considering not just unit price but also compliance risk, brand uplift, and waste management savings. For more insights on sourcing sustainable options, read our guide on sustainable” target=”_blank” class=”text-primary-dark hover:underline”>sustainable coffee straws for B2B.
D. Comparison Table: Key Sustainable Coffee Straw Types for B2B
| Besonderheit | B2B Betriebswirkung | Compliance Note | ROI -Potenzial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coffee Grounds | Reduces waste stream, subtle coffee aroma, durable in hot/cold drinks up to 75°C. | 100% compostable (e.g., ASTM D6400, BPI), plastic-free, PFAS-free. | Enhanced brand image, waste diversion, premium perception, customer loyalty. |
| Essbare Strohhalme | Zero-waste, high novelty factor, individual hygiene. Holds for hours in cold, 1 hr in hot. | Fully biodegradable, consumable; check allergen compliance. | Premium offering, viral marketing potential, eliminates waste collection. |
| Zuckerrohr (Bagasse) | High heat resistance (up to 90°C), minimal sogginess, sturdy. | 100% compostable, no PLA/PFAS, complies with plastic bans. | Appeals to eco-conscious consumers, robust performance, cost-effective in bulk. |
| PLA (Bioplastic) | Similar feel to plastic, clear options, widely available. | Industrial composting required; may soften >60°C; restricted in some bans. | Widely available, meets some “green” criteria, good for cold drinks. |
| Reusable (Metal/Silicone) | High initial cost, requires washing/storage infrastructure, potential heat conductivity issue (metal). | Long-term waste elimination; specific cleaning protocols needed. | Significant long-term cost savings, strong sustainability messaging, reduces repeat purchases. |
Evaluating performance, compliance, and cost is essential for B2B sustainable straw procurement.
IV. Driving Adoption: B2B Opportunities and Future of Coffee Straws
The imperative to transition to sustainable straws extends beyond mere compliance; it’s a profound opportunity for businesses to gain a competitive edge, deepen customer loyalty, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
A. Enhanced Brand Image & Customer Loyalty: The Sustainability Dividend
Adopting eco-friendly solutions directly improves a company’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) profile. This resonates deeply with today’s consumers, especially younger demographics who are increasingly prioritizing environmental impact in their purchasing decisions. Businesses that actively reduce their plastic footprint, using certified compostable options like coffee grounds or sugarcane straws, gain a significant competitive advantage. This communicates a genuine commitment to reducing plastic pollution, impacting marine life, and fostering a circular economy. Such tangible actions can attract new, loyal customers and reinforce positive brand perception, transforming a compliance challenge into a powerful marketing asset.
B. Mini Case Study: Starbucks’ Evolution in Sustainable Straws
Starbucks, a global coffee giant, has been a bellwether in the industry’s struggle with single-use plastics. In 2018, the company committed to eliminating 1 billion plastic straws annually by 2020, initially introducing strawless lids and FSC® certified paper straws. This move was a significant step towards their broader sustainability goals, which include a 50% reduction in waste, carbon emissions, and water usage by 2030.
However, the journey has not been without its challenges. In a significantpilot program in June 2025, Starbucks Korea reintroduced sugarcane-based plastic straws in approximately 200 stores. This decision came in response to persistent customer complaints about the performance of soggy paper straws, highlighting the ongoing tension between sustainability, customer experience, and operational feasibility. This case underscores a vital lesson for B2B decision-makers: true sustainable innovation must balance environmental responsibility with uncompromised product performance. Sourcing heat-resistant, non-soggy options like those available atMomoio” target=”_blank” class=”text-primary-dark hover:underline”>Momoio Heat-Resistant Coffee Strawsis crucial.
C. Future Trends in Sustainable Coffee Straw Innovation: 2025-2035 Outlook
The next 5-10 years will witness an acceleration of innovation in sustainable coffee straws, driven by evolving regulations and material science breakthroughs.
- Market Growth: The eco-friendly straw market is projected to reach nearly $25.1 billion by 2035, growing at a robust CAGR of 7.3%. Biodegradable straws (including paper, bamboo, PHA, and PHBH) are expected to capture a commanding 60% market share by 2030.
- Advanced Materials & Coatings: Expect a strong focus on advanced water-resistant coatings for paper straws and hybrid materials for enhanced durability. Next-generation bioplastics like PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoate) and PHBH (Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyhexanoate), derived from biomass, will gain prominence for their plastic-like performance and broad biodegradability in diverse environments, including marine water.
- Waste Valorization: Innovations leveraging waste streams, such as coffee grounds and sugarcane bagasse, will continue to expand, promoting a circular economy.
- AI-Fueled Manufacturing: Artificial intelligence will play an increasing role in material research, driving the discovery of novel bio-based polymers and optimizing production efficiency for sustainable straws.
- Integrated Solutions: The market will see more multi-use straw solutions, including collapsible reusable straws, and integrated tumbler-straw products, offering enhanced convenience for on-the-go consumption.
- Smart Composting: Advances in smart composting technologies will make it easier for businesses to handle compostable straws, closing the loop on their lifecycle.
Future trends indicate significant growth and innovation in sustainable coffee straw materials and solutions.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Coffee Experience with Sustainable Choices
The transition away from single-use plastics is not just a passing trend; it’s a fundamental shift reshaping business operations and consumer expectations across the globe. By understandingwhat coffee straws are made ofand embracing innovative, high-performance sustainable options like coffee grounds and edible straws, your business can achieve critical regulatory compliance, enhance operational efficiency, and capture the loyalty of a growing eco-conscious market. This proactive approach mitigates risks, quantifies cost savings through reduced waste, and significantly uplifts brand value, positioning your enterprise as a market leader in sustainability.
Embracing sustainable coffee straws ensures compliance, boosts efficiency, and enhances brand loyalty.
Act now to future-proof your procurement strategy.Momoio.com” target=”_blank” class=”btn-primary inline-block”>Explore Truly Compostable Options for Your Coffee Shop
Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs)
Q: How do coffee grounds straws perform in hot beverages compared to paper straws?
A: Coffee grounds straws are engineered to withstand temperatures up to 75°C (167°F) and are significantly more resistant to sogginess than traditional paper straws, providing a consistent and enjoyable experience for hot coffee drinkers in hospitality settings.
Q: Are edible coffee straws a hygienic option for high-volume foodservice operations?
A: Yes, many edible straws are individually wrapped, which addresses hygiene concerns for high-volume operations. They also boast a shelf life of up to two years, making them a practical and zero-waste solution for cafes and restaurants.
Q: What certifications should procurement managers look for to ensure sustainable straw compliance?
A: Key certifications include BPI (Biodegradable Products Institute) for industrial compostability in North America (ASTM D6400/D6868), EN13432 for European industrial compostability, FDA approval for food safety, and explicit plastic-free verification to meet global plastic ban regulations.
Q: How can adopting sustainable straws impact a hospitality business’s brand image and customer loyalty?
A: Adopting eco-friendly straws significantly enhances a company’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) profile, resonating with eco-conscious consumers. This can attract new, loyal customers and reinforce positive brand perception, transforming a compliance challenge into a powerful marketing asset.
Q: What are the long-term cost benefits of switching to compostable straws for foodservice operations?
A: While upfront costs might be higher, compostable straws can reduce waste disposal fees by diverting materials from landfills. The enhanced brand image also attracts environmentally conscious customers, potentially increasing revenue and market share without heavy marketing spend, leading to compelling long-term ROI






