A critical guide for procurement managers, operations directors, and sustainability officers in hospitality & foodservice.
The global push for sustainability has significantly reshaped procurement strategies across industries, with businesses increasingly seeking eco-friendly alternatives to single-use plastics. Bamboo straws have emerged as a prominent candidate, often marketed as a simple, natural solution. However, for astute B2B decision-makers—including procurement managers, operations directors, and sustainability officers—a deeper, data-backed analysis reveals significant and often overlooked drawbacks. Relying solely on the “eco-friendly” label without scrutinizing operational, hygienic, and economic implications can expose organizations to unforeseen risks and undermine their genuine sustainability objectives. Understanding these critical disadvantages is paramount for informed and responsible sourcing that protects both consumers and corporate reputation.
This analysis is particularly crucial for thehospitality and foodservice industries, where consumer health, brand reputation, and operational efficiency are paramount. Ignoring these disadvantages can lead to increased operational costs, negative customer experiences, and potential regulatory non-compliance, ultimately hindering genuine sustainability efforts and competitive standing.
Informed sourcing protects consumers and reputation, crucial for hospitality and foodservice.
Hidden Health Hazards: The Overlooked Bamboo Straw Disadvantage
While seemingly benign, bamboo straws can harbor serious health risks, a critical concern for any business prioritizing consumer safety and regulatory compliance.
PFAS Contamination: A “Forever Chemical” Concern
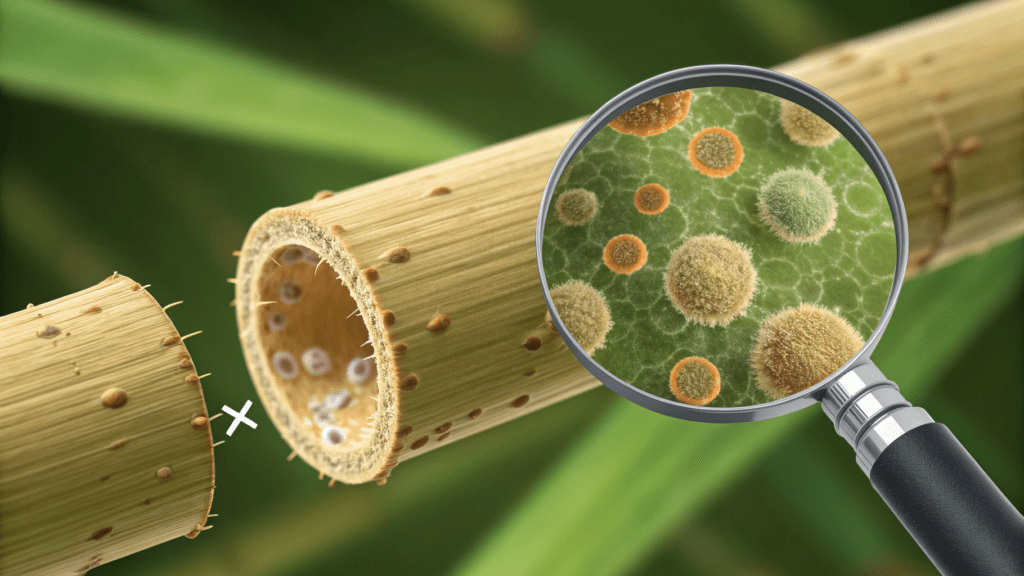
Recent scientific findings have cast a long shadow over the perceived purity of bamboo straws. A groundbreaking study published inFood Additives and Contaminantsin August 2023 revealed that 80% of tested bamboo straw brands contained poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). These insidious “forever chemicals” are not only environmentally persistent, degrading over thousands of years, but are also linked to severe human health issues, including lower vaccine response, thyroid disease, elevated cholesterol levels, liver damage, and certain cancers. Critically, the study detected perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a globally banned PFAS since 2020, undermining any claims of inherent biodegradability and posing significant regulatory and reputational risks for businesses. Furthermore, highly water-soluble PFAS like trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TFMS) were also found, indicating a potential for these harmful compounds to leach directly into beverages, exposing consumers to immediate health hazards.
Significant Bamboo Straw Hygiene Challenges
Beyond chemical contamination, the fundamental material properties of bamboo present inherent hygiene obstacles. Bamboo’s porous and fibrous nature makes thorough cleaning exceptionally difficult, often necessitating specialized brushes and meticulous care. Unlike non-porous materials such as glass or stainless steel, bamboo readily absorbs liquids and organic residues. If not completely dried after each use, these absorbed materials create ideal breeding grounds for mold and bacteria, posing substantial health risks to consumers. The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) explicitly recommends against using multiple-use straws if thorough cleaning cannot be guaranteed, a particularly challenging directive for high-volume commercial environments likerestaurants and hotels. The requirement for meticulous handwashing and complete drying — as bamboo straws are not dishwasher-safe — adds significant labor, operational complexity, and cost to any business attempting to integrate them into a reusable program.
Bamboo straws pose health risks from PFAS and hygiene issues, impacting hospitality safety.
Durability and Operational Lifespan: A Key Bamboo Straw Disadvantage for Businesses
For B2B operations, durability directly translates to cost-efficiency and consistent service quality. Bamboo straws fall short in this critical area.
Fragility and Rapid Degradation
Bamboo straws exhibit a significantly shorter operational lifespan compared to more robust reusable alternatives like metal or glass, typically lasting only “several months to a year” even with careful handling. Frequent use, particularly with hot liquids, accelerates their degradation, leading to common issues such as cracking, splintering, and softening. This inherent fragility necessitates far more frequent replacements, directly inflating operational costs and paradoxically contributing to waste streams that businesses aim to reduce. Beyond the economic burden, damaged straw surfaces compromise hygiene and pose immediate safety risks to users, demanding immediate removal from service to prevent injuries or further contamination. This constant need for replacement creates a logistical headache and a hidden financial drain on procurement budgets forfoodservice establishments.
Short lifespan and fragility of bamboo straws inflate operational costs significantly.
The Complex Environmental Footprint of Bamboo Straws
While often lauded as an “eco-friendly” choice, a comprehensive life-cycle assessment reveals a more nuanced and often less sustainable reality for bamboo straws.
Production & Transportation Carbon Footprint
The journey of a bamboo straw from cultivation to consumer often carries a significant, hidden carbon footprint. While bamboo itself is a renewable resource, the processes of harvesting, shaping, and most notably, international shipping, are energy-intensive. Large-scale bamboo plantations are predominantly located in Asia and South America. Transporting these finished products across continents to markets in North America and Europe results in extensive long transport routes and considerable CO2 emissions. Furthermore, some production practices can involve clearing natural forests for monoculture plantations, depleting biodiversity, and the transformation process itself can utilize chemicals and energy. A Greek life-cycle assessment (LCA) critically indicated that bamboo and other bioplastic alternatives could have “up to 2.5 times higher climate impacts” than traditional plastic straws when considering their full life cycle. This is a crucial consideration forhospitality supply chainsaiming for true sustainability.
Biodegradability vs. Practical Disposal Challenges
The term “biodegradable” for bamboo straws often misrepresents their real-world disposal complexities. While they may be technically compostable, efficient breakdown in standard home composting systems is rarely achieved. For true decomposition, bamboo straws typically require specialized industrial composting facilities that operate at specific temperatures and humidity levels. Crucially, access to such facilities is not universally widespread in many regions, including significant parts of the US and EU. Without proper industrial composting infrastructure, these “biodegradable” straws often end up in general waste landfills, where they may degrade slowly in anaerobic conditions, potentially releasing methane (a potent greenhouse gas) or breaking down into microplastics rather than fully returning to nature. This gap between marketing claims and practical disposal realities highlights a critical failure point in their supposed environmental benefit forfoodservice operations.
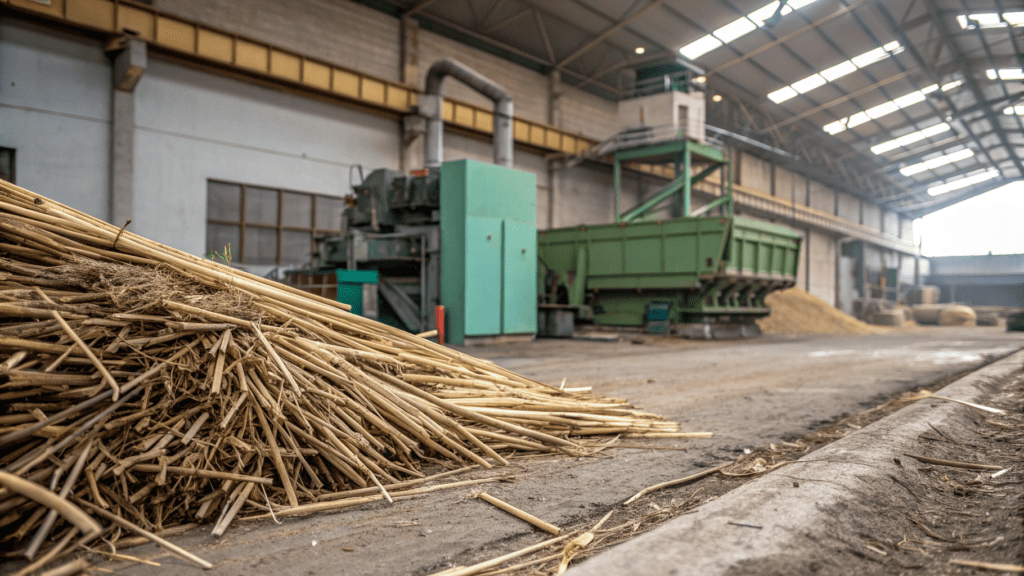

Bamboo straws’ environmental footprint is complex, with hidden carbon and disposal challenges.
User Experience and Practical Limitations: Understanding the Disadvantage of Bamboo Straw
Beyond the hidden health and environmental issues, the day-to-day user experience with bamboo straws can significantly detract from customer satisfaction and brand perception.
Taste Transfer and Inconsistent Quality
One of the most common user complaints is the “subtle taste” or distinct “woody” flavor that bamboo straws can impart to beverages. This taste transfer can noticeably detract from the enjoyment of drinks, particularly those with delicate flavors like specialty coffees, teas, or fine spirits. Forhospitality businesses, this directly impacts customer experience and can lead to dissatisfaction. Moreover, the natural variations in bamboo lead to inconsistent quality, appearance, and mouthfeel. Users frequently report uneven diameters, making it challenging to sip thicker beverages like smoothies or milkshakes, and some describe the texture as “chalky” or generally unappealing. Such inconsistencies reflect poorly on a business that aims for a premium and uniform customer experience.
Sensitivity to Beverages and Use Cases
Bamboo straws exhibit limited heat resistance. They are not ideal for very hot drinks, as prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause them to soften, crack, or even splinter, posing safety risks. Their opaque and porous nature also makes it exceedingly difficult for staff or consumers to visually confirm thorough cleanliness after use, fostering a perception of unhygienic conditions. Furthermore, their inherent rigidity and lack of flexibility may pose safety risks for certain individuals, particularly those with disabilities, limiting accessibility and inclusivity for businesses committed to serving all customers infoodservice environments.
Bamboo straws compromise user experience through taste transfer and practical limitations.
Economic Considerations and Commercial Viability
The perceived environmental benefits of bamboo straws often mask significant economic disadvantages that impact the bottom line for B2B operations.
Higher Procurement Costs and ROI Implications
Contrary to initial assumptions, bamboo straws are generally “more expensive” upfront than traditional plastic straws and even many other reusable options. A detailed cost analysis cited in academic research indicated that bamboo straws could incur an annual cost of “EUR 7.97 per year” per straw, significantly higher than “EUR 0.30 per year” for single-use plastic straws, or even reusable silicone (EUR 1.17) and metal (EUR 2.81) alternatives. This higher initial investment, compounded by the necessity for frequent replacement due to their fragility, drastically inflates the actual cost-per-use for businesses, eroding potential ROI and straining procurement budgets forhospitality and foodservice operations.
Limited Commercial Approval and Accessibility
A significant barrier to widespread B2B adoption is the “limited commercial approval” for bamboo drinking straws. Due to pervasive “hygienic concerns,” they are “often not approved for use in the catering trade” in many regions. This regulatory and industry skepticism stems from the material’s inherent cleaning difficulties and potential for microbial growth. Beyond approval, the limited availability of bamboo resources outside of Asia and South America can complicate procurement and logistics for businesses in other parts of the world, leading to supply chain vulnerabilities and increased shipping costs. The absence of comprehensive, universally enforced quality and hygiene standards across the bamboo straw market further exacerbates these inconsistencies, making it difficult for businesses to source reliable, compliant products consistently. For full regulatory details, consult ourcomprehensive guide on regulatory compliance for sustainable products.
Bamboo straws present significant economic drawbacks due to high costs and limited commercial viability.
Comparison Table: Reusable Straw Alternatives for B2B Sourcing
When re-evaluating straw procurement, discerning B2B decision-makers must consider a range of factors beyond just “eco-friendly” claims. The following table provides a direct comparison of common reusable straw alternatives, highlighting their operational, compliance, and ROI implications. While many organizations initially considered options like bamboo among the leading eco-friendly alternatives to plastic, the evolving understanding of their true lifecycle impact and practical limitations demands a more rigorous evaluation of available materials for your sustainablehospitality procurement guide.
| Özellik | B2B operasyonel etki | Uyum Notu | YG'nin potansiyeli |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bambu Pipetler | High maintenance (meticulous hand wash, special brushes), frequent replacement, inconsistent quality, taste transfer | Not approved in some catering trades (hygiene); high PFAS contamination risk (80% of brands). | Low (high replacement rate, labor-intensive cleaning, higher initial cost; EUR 7.97/year) |
| Metal Straws | Highly durable (years of use), very easy to clean (dishwasher safe), consistent quality & mouthfeel | Generally food-safe; potential for heat conduction with hot drinks. | High (very long lifespan, low maintenance, reusable for years; EUR 2.81/year) |
| Cam Pipetler | Durable, transparent (easy to check cleanliness), elegant presentation, consistent quality | Breakable (potential safety risk if chipped); generally food-safe. | Medium-High (long lifespan, easy cleaning, aesthetic appeal, good for high-end venues) |
| Silicone Straws | Flexible, highly durable, dishwasher safe, soft mouthfeel, versatile for all ages | Food-grade silicone; can attract lint; not ideal for very hot drinks. | High (long lifespan, low maintenance, versatile, low replacement; EUR 1.17/year) |
| Kağıt Pipetler | Single-use, prone to softening quickly, significant taste transfer, poor user experience | Variable biodegradability; very high PFAS common (found in 90% of brands). | Very Low (single-use, poor user experience, high cost per use; frequent re-stocking) |
Choosing the right straw alternative is crucial for B2B operational efficiency and ROI.
Mini Case Study: The Unforeseen Costs of a Bamboo Straw Pilot
A prominent fast-casual dining chain, aiming for a 20% reduction in single-use plastic by 2024, piloted bamboo straws across 15 locations. While initially applauded for their eco-friendly image and public relations appeal, operational data within seven months revealed significant, unexpected drawbacks. Cleaning staff reported persistent issues with the porous material absorbing residue, making visual cleanliness checks difficult and contributing to a 15% increase in cleaning labor hours for straws alone. Durability proved a major concern, with the average lifespan being just 2-3 months before cracking or splintering, leading to replacement costs 4x higher than projected (due to the “EUR 7.97 per year” cost compared to former plastic options). Guest feedback indicated clear dissatisfaction, with 18% reporting a “woody taste” and 10% expressing hygiene concerns, significantly impacting overall customer experience and potentially repeat business. This forced the chain to pivot its strategy towards more durable, easily sanitizable alternatives, despite the initial public relations appeal of bamboo. The experience underscored the vital need for comprehensive lifecycle and operational analysis before committing to “green” alternatives.
A pilot revealed bamboo straws’ hidden costs and negative customer impact.
Future Trends & Innovation in Sustainable Straw Solutions
The landscape of sustainable sourcing is rapidly evolving, driven by escalating consumer demand for genuine eco-friendly products and increasingly stringent global regulations. Over the next 5-10 years, several key trends will define the future of sustainable straw alternatives, moving beyond the limitations of early-stage options like bamboo.
Firstly,regulatory pressureon “forever chemicals” like PFAS will intensify globally. The alarming prevalence of PFAS in plant-based straws will likely lead to stricter EU and US regulations regarding chemical content in food contact materials. This will force manufacturers to innovate towards truly chemical-free and safely compostable or reusable solutions, shifting away from materials that pose hidden health and environmental risks.
Secondly, the focus will move from mere “biodegradability” totrue circularity and industrial compostability. Businesses will demand alternatives that genuinely integrate into existing waste management infrastructures or enable robust closed-loop recycling systems. This means a greater emphasis on certified industrial compostability (e.g., BPI certified) and potentially advanced bio-plastics or even more refined natural materials that break down reliably without leaving harmful residues. Our guide oneco-friendly restaurant supplies, including sugarcane and bamboo straws, further explores materials better suited for genuine sustainability.
Thirdly,advancements in material sciencewill introduce new generations of bio-based materials. We will see increased investment in innovative plant-based polymers and composites that offer superior durability, heat resistance, and cleanability compared to current bamboo or basic paper straws, all while minimizing their environmental footprint. Expect materials derived from agricultural waste or novel plant fibers that offer industrial-grade performance.
Finally,supply chain transparency and localized sourcingwill gain prominence. As businesses seek to reduce their carbon footprint and enhance ethical sourcing, the long international shipping routes associated with bamboo will become increasingly unattractive. The market will favor solutions from regions with established sustainable cultivation and manufacturing practices, leading to more regionalized supply chains that mitigate environmental impact and logistical complexities. This holistic approach ensures that “sustainable” labels translate into tangible environmental and operational benefits.
Future trends emphasize chemical-free, circular, and localized sustainable straw solutions.
Competitive Advantage & Business Case for Strategic Straw Sourcing
For procurement managers and supply chain executives, a thorough understanding of bamboo straw disadvantages isn’t just about avoiding pitfalls; it’s about seizing a significant competitive advantage. By moving beyond superficially green solutions and embracing genuinely sustainable, operationally sound alternatives, businesses can unlock substantial value:
- Risk Mitigation & Compliance:Proactively addressing issues like PFAS contamination and hygiene concerns helps organizations avoid costly fines, potential litigation, and severe reputational damage. Aligning with emerging global regulations positions your brand as a responsible leader, mitigating future compliance risks.
- Cost Optimization & ROI:While upfront costs may vary, selecting durable, easy-to-clean alternatives significantly reduces long-term operational expenses. Reduced replacement rates and lower labor costs for cleaning translate directly into quantifiable savings. The mini case study clearly illustrates how a seemingly cheaper “eco-friendly” option can inflate costs by 4x. Strategic investment in the right alternatives offers a far superior ROI over the typical “several months to a year” lifespan of bamboo.
- Enhanced Brand Value & Customer Loyalty:Consumers are increasingly discerning. Offering genuinely safe, high-quality, and truly sustainable products enhances customer experience, builds trust, and strengthens brand loyalty. Avoiding issues like taste transfer, hygiene concerns, or splintering protects your brand image and fosters positive word-of-mouth. This provides a clear competitive edge in a market where consumers prioritize authenticity and health.
- Operational Efficiency:Standardized, easy-to-clean, and durable straws simplify inventory management, reduce staff training time, and streamline daily operations. This frees up resources and improves overall service delivery, contributing directly to an optimized operational flow.
- Market Leadership:By demonstrating a commitment to rigorous, data-driven sustainability, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors who might still be using less-vetted “green” alternatives. This positions your organization as an innovator and a leader in responsible environmental stewardship, potentially capturing greater market share from discerning B2B and B2C clients alike. For a broader overview of alternatives to plastic, explore the range of options beyond bamboohere.
Final CTA
Evaluate your organization’s straw procurement strategy today to ensure compliance, optimize operational efficiency, and genuinely align with sustainable, safe practices for a competitive edge in the evolving market.
Strategic straw sourcing offers competitive advantages through risk mitigation and enhanced brand value.
Sık Sorulan Sorular (SSS)
What are the main health risks associated with bamboo straws for hospitality businesses?
Bamboo straws can harbor PFAS “forever chemicals” (found in 80% of tested brands) and pose significant hygiene challenges due to their porous nature, leading to mold and bacteria growth if not meticulously cleaned and dried, which is difficult in high-volume commercial settings.
How do bamboo straws impact operational costs for foodservice procurement managers?
Bamboo straws have a short lifespan (2-3 months in commercial use), requiring frequent replacement. Their high initial cost (EUR 7.97/year per straw) combined with labor-intensive cleaning significantly inflates operational expenses compared to more durable alternatives.
Are bamboo straws truly biodegradable in commercial waste streams?
While technically compostable, bamboo straws typically require specialized industrial composting facilities. Without access to these, they often end up in landfills, where they may degrade slowly and potentially release methane or microplastics, undermining their environmental claims.
What are the user experience drawbacks of bamboo straws in a restaurant or hotel setting?
Bamboo straws can impart a “woody” taste, have inconsistent quality, and are not ideal for hot beverages. Their opaque nature makes cleanliness difficult to verify, impacting customer perception and satisfaction.
What sustainable straw alternatives offer better ROI and compliance for B2B hospitality?
Metal, glass, and silicone straws offer superior durability, easier cleaning (often dishwasher-safe), and better long-term ROI. Sugarcane straws are also emerging as a strong single-use, compostable alternative without the hygiene or PFAS concerns.
FAQs address key concerns for hospitality and foodservice straw sourcing.






